A homology-based pipeline for global prediction of post-translational modification sites
- PMID: 27174170
- PMCID: PMC4865729
- DOI: 10.1038/srep25801
A homology-based pipeline for global prediction of post-translational modification sites
Abstract
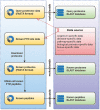
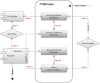
The pathways of protein post-translational modifications (PTMs) have been shown to play particularly important roles for almost any biological process. Identification of PTM substrates along with information on the exact sites is fundamental for fully understanding or controlling biological processes. Alternative computational strategies would help to annotate PTMs in a high-throughput manner. Traditional algorithms are suited for identifying the common organisms and tissues that have a complete PTM atlas or extensive experimental data. While annotation of rare PTMs in most organisms is a clear challenge. In this work, to this end we have developed a novel homology-based pipeline named PTMProber that allows identification of potential modification sites for most of the proteomes lacking PTMs data. Cross-promotion E-value (CPE) as stringent benchmark has been used in our pipeline to evaluate homology to known modification sites. Independent-validation tests show that PTMProber achieves over 58.8% recall with high precision by CPE benchmark. Comparisons with other machine-learning tools show that PTMProber pipeline performs better on general predictions. In addition, we developed a web-based tool to integrate this pipeline at http://bioinfo.ncu.edu.cn/PTMProber/index.aspx. In addition to pre-constructed prediction models of PTM, the website provides an extensional functionality to allow users to customize models.
Figures

Similar articles
-
PTM-ssMP: A Web Server for Predicting Different Types of Post-translational Modification Sites Using Novel Site-specific Modification Profile.Int J Biol Sci. 2018 May 22;14(8):946-956. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.24121. eCollection 2018. Int J Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29989096 Free PMC article.
-
Large-scale comparative assessment of computational predictors for lysine post-translational modification sites.Brief Bioinform. 2019 Nov 27;20(6):2267-2290. doi: 10.1093/bib/bby089. Brief Bioinform. 2019. PMID: 30285084 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PhosphOrtholog: a web-based tool for cross-species mapping of orthologous protein post-translational modifications.BMC Genomics. 2015 Aug 19;16(1):617. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1820-x. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26283093 Free PMC article.
-
dbPTM 2016: 10-year anniversary of a resource for post-translational modification of proteins.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jan 4;44(D1):D435-46. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1240. Epub 2015 Nov 17. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 26578568 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review on Posttranslational Modification in Proteins: Feature Construction, Algorithm and Webserver.Protein Pept Lett. 2018;25(9):807-814. doi: 10.2174/0929866525666180925151720. Protein Pept Lett. 2018. PMID: 30255739
Cited by
-
Proteoform-predictor: Increasing the Phylogenetic Reach of Top-Down Proteomics.J Proteome Res. 2025 Apr 4;24(4):1861-1870. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.4c00943. Epub 2025 Mar 10. J Proteome Res. 2025. PMID: 40062899 Free PMC article.
-
A single structurally conserved SUMOylation site in CRMP2 controls NaV1.7 function.Channels (Austin). 2017 Jul 4;11(4):316-328. doi: 10.1080/19336950.2017.1299838. Epub 2017 Feb 28. Channels (Austin). 2017. PMID: 28277940 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jensen O. N. Modification-specific proteomics: characterization of post-translational modifications by mass spectrometry. Curr Opin Chem Biol 8, 33–41 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Liu C. & Li H. In silico prediction of post-translational modifications. Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, N.J.) 760, 325–340 (2011). - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

