Family partnership and education interventions to reduce dietary sodium by patients with heart failure differ by family functioning
- PMID: 27174641
- PMCID: PMC4935570
- DOI: 10.1016/j.hrtlng.2016.04.001
Family partnership and education interventions to reduce dietary sodium by patients with heart failure differ by family functioning
Abstract
Objectives: Determine if family functioning influences response to family-focused interventions aimed at reducing dietary sodium by heart failure (HF) patients.
Background: Lowering dietary sodium by HF patients often occurs within the home and family context.
Methods: Secondary analysis of 117 dyads randomized to patient and family education (PFE), family partnership intervention (FPI) or usual care (UC). Dietary sodium measures were obtained from 3-day food record and 24-h urine samples.
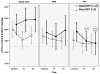
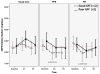
Results: In the poor family functioning groups, FPI and PFE had lower mean urine sodium than UC (p < .05) at 4 months, and FPI remained lower than UC at 8 months (p < .05). For good family functioning groups, FPI and PFE had lower mean sodium levels by 3-day food record at 4 and 8 months compared to the UC group.
Conclusion: Optimizing family-focused interventions into HF clinical care maybe indicated.
Keywords: Adherence; Dietary sodium; Family functioning; Heart failure; Self-care.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Lindenfeld J, Albert NM, Boehmer JP, et al. HFSA 2010 Comprehensive Heart Failure Practice Guideline. J Card Fail. 2010;16(6):e1–194. - PubMed
-
- Bentley B, De Jong MJ, Moser DK, Peden AR. Factors related to nonadherence to low sodium diet recommendations in heart failure patients. Eur J Cardiov Nurs. 2005;4(4):331–336. - PubMed
-
- Ryan RM, Deci EL. Self-determination theory and the facilitation of intrinsic motivation, social development, and well-being. Am Psychol. 2000;55(1):68. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

