p70S6K promotes IL-6-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 27174914
- PMCID: PMC5095019
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.9282
p70S6K promotes IL-6-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
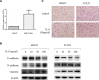
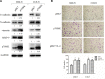
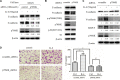
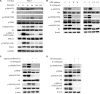
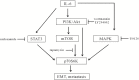
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) is the fifth most common cancer worldwide and a common cause of cancer-related death, with a 5-year survival rate of less than 60%. IL-6 has been suggested to play an important role in cancer metastasis, but its mechanism in HNSCC has not been fully clarified. p70S6K has been reported to induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of ovarian cancer, but its role in HNSCC remains unknown. In this study, we found that p70S6K and IL-6 were upregulated in high-metastatic HNSCC cell lines that underwent EMT when compared to paired low-metastatic cell lines. Overexpression of p70S6K promoted EMT and migration of HNSCC cells, while downregulation of p70S6K attenuated IL-6-induced EMT and cell migration. Furthermore, IL-6-induced p70S6K activation was attenuated by inhibitors of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR, MAPK/ERK, and JAK/STAT3 signaling pathways, suggesting that it located downstream of these pathways. These findings suggest that p70S6K promotes IL-6-induced EMT and metastasis of HNSCC. Targeting p70S6K for HNSCC therapy may benefit patients through the inhibition of tumor growth, as well as metastasis.
Keywords: HNSCC; IL-6; epithelial-mesenchymal transition; metastasis; p70S6K.
Conflict of interest statement
There were no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
IGF2BP1 promotes the progression of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by activating PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway and inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition.World J Surg Oncol. 2025 Jul 14;23(1):277. doi: 10.1186/s12957-025-03929-5. World J Surg Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40660234 Free PMC article.
-
Emodin represses TWIST1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells by inhibiting the β-catenin and Akt pathways.Eur J Cancer. 2014 Jan;50(2):366-78. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2013.09.025. Epub 2013 Oct 21. Eur J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24157255
-
Bicarbonate transporter SLC4A7 promotes EMT and metastasis of HNSCC by activating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.Mol Carcinog. 2023 May;62(5):628-640. doi: 10.1002/mc.23511. Epub 2023 Feb 2. Mol Carcinog. 2023. PMID: 36727616
-
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem(-like) cells in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Cancer Lett. 2013 Sep 10;338(1):47-56. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2012.06.013. Epub 2012 Jul 4. Cancer Lett. 2013. PMID: 22771535 Review.
-
The PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis in head and neck cancer: functions, aberrations, cross-talk, and therapies.Oral Dis. 2015 Oct;21(7):815-25. doi: 10.1111/odi.12206. Epub 2013 Dec 23. Oral Dis. 2015. PMID: 24219320 Review.
Cited by
-
IL-6 and ovarian cancer: inflammatory cytokines in promotion of metastasis.Cancer Manag Res. 2018 Dec 5;10:6685-6693. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S179189. eCollection 2018. Cancer Manag Res. 2018. PMID: 30584363 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ZnO Nanoparticles Induced Caspase-Dependent Apoptosis in Gingival Squamous Cell Carcinoma through Mitochondrial Dysfunction and p70S6K Signaling Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 26;21(5):1612. doi: 10.3390/ijms21051612. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32111101 Free PMC article.
-
NVP-BEZ235, a dual PI3K-mTOR inhibitor, suppresses the growth of FaDu hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma and has a synergistic effect with Cisplatin.Cell Death Discov. 2018 May 10;4:57. doi: 10.1038/s41420-018-0060-7. eCollection 2018. Cell Death Discov. 2018. PMID: 29760955 Free PMC article.
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway in oral cancer.Oncol Lett. 2018 Feb;15(2):1379-1388. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.7491. Epub 2017 Nov 24. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29434828 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-449a antagonizes EMT through IL-6-mediated trans-signaling in laryngeal squamous cancer.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2024 Feb 6;35(1):102140. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2024.102140. eCollection 2024 Mar 12. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2024. PMID: 38425711 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gaykalova DA, Manola JB, Ozawa H, Zizkova V, Morton K, Bishop JA, Sharma R, Zhang C, Michailidi C, Considine M, Tan M, Fertig EJ, Hennessey PT, et al. NF-kappaB and stat3 transcription factor signatures differentiate HPV-positive and HPV-negative head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2015;137:1879–1889. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Leemans CR, Braakhuis BJ, Brakenhoff RH. The molecular biology of head and neck cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011;11:9–22. - PubMed
-
- Kalavrezos N, Bhandari R. Current trends and future perspectives in the surgical management of oral cancer. Oral Oncol. 2010;46:429–432. - PubMed
-
- Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY, Nieto MA. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell. 2009;139:871–890. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

