The effect of insulin-loaded linear poly(ethylene glycol)-brush-like poly(l-lysine) block copolymer on renal ischemia/reperfusion-induced lung injury through downregulating hypoxia-inducible factor
- PMID: 27175073
- PMCID: PMC4854262
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S99890
The effect of insulin-loaded linear poly(ethylene glycol)-brush-like poly(l-lysine) block copolymer on renal ischemia/reperfusion-induced lung injury through downregulating hypoxia-inducible factor
Abstract
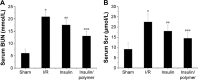
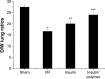
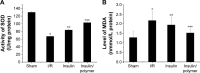
The aim of this study was to observe the therapeutic effect of insulin-loaded linear poly(ethylene glycol)-brush-like poly(l-lysine) block copolymer poly(ethylene glycol)-b-(poly(ethylenediamine l-glutamate)-g-poly(l-lysine)) (PEG-b-(PELG-g-PLL) on renal ischemia/reperfusion-induced lung injury through downregulating hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) as compared to free insulin. Sprague Dawley rats were pretreated with 30 U/kg insulin or insulin/PEG-b-(PELG-g-PLL) complex, and then subjected to 45 minutes of ischemia and 24 hours of reperfusion. The blood and lungs were collected, the level of serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen were measured, and the dry/wet lung ratios, the activity of superoxide dismutase and myeloperoxidase, the content of methane dicarboxylic aldehyde and tumor necrosis factor-α, and the expression of HIF-1α and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) were measured in pulmonary tissues. Both insulin and insulin/PEG-b-(PELG-g-PLL) preconditioning improved the recovery of renal function, reduced pulmonary oxidative stress injury, restrained inflammatory damage, and downregulated the expression of HIF-1α and VEGF as compared to ischemia/reperfusion group, while insulin/PEG-b-(PELG-g-PLL) significantly improved this effect.
Keywords: HIF-1α; RI/RILI; VEGF; block copolymer; insulin.
Figures






Similar articles
-
PEG-b-(PELG-g-PLL) nanoparticles as TNF-α nanocarriers: potential cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury therapeutic applications.Int J Nanomedicine. 2017 Mar 23;12:2243-2254. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S130842. eCollection 2017. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017. PMID: 28356740 Free PMC article.
-
Sustained delivery of insulin-loaded block copolymers: Potential implications on renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in diabetes mellitus.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Jul;91:534-545. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.04.118. Epub 2017 May 5. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28482291
-
Poly (Ethylene Glycol)-Block-Brush Poly (L-Lysine) Copolymer as an Efficient Nanocarrier for Human Hepatocyte Growth Factor with Enhanced Bioavailability and Anti-Ischemia Reperfusion Injury Efficacy.Kidney Blood Press Res. 2017;42(3):495-508. doi: 10.1159/000479642. Epub 2017 Aug 30. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2017. PMID: 28854424
-
Polyethylene glycol-superoxide dismutase, a conjugate in search of exploitation.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2002 Jun 17;54(4):587-606. doi: 10.1016/s0169-409x(02)00029-7. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2002. PMID: 12052716 Review.
-
Nitroxyl radical-containing nanoparticles for novel nanomedicine against oxidative stress injury.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2011 Apr;6(3):509-18. doi: 10.2217/nnm.11.13. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2011. PMID: 21542688 Review.
Cited by
-
In vitro/vivo drug release and anti-diabetic cardiomyopathy properties of curcumin/PBLG-PEG-PBLG nanoparticles.Int J Nanomedicine. 2018 Apr 3;13:1945-1962. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S153763. eCollection 2018. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018. Retraction in: Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 May 25;16:3579. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S320050. PMID: 29662310 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Chitosan-microcapsulated insulin alleviates mesenteric microcirculation dysfunction via modulating COX-2 and VCAM-1 expression in rats with diabetes mellitus.Int J Nanomedicine. 2018 Oct 25;13:6829-6837. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S174030. eCollection 2018. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018. PMID: 30498345 Free PMC article.
-
Poly(α-l-lysine)-based nanomaterials for versatile biomedical applications: Current advances and perspectives.Bioact Mater. 2020 Dec 13;6(7):1878-1909. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2020.12.001. eCollection 2021 Jul. Bioact Mater. 2020. PMID: 33364529 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lumbrokinase/paclitaxel nanoparticle complex: potential therapeutic applications in bladder cancer.Int J Nanomedicine. 2018 Jun 26;13:3625-3640. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S166438. eCollection 2018. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018. PMID: 29983558 Free PMC article.
-
Quercetin nanoparticle complex attenuated diabetic nephropathy via regulating the expression level of ICAM-1 on endothelium.Int J Nanomedicine. 2017 Oct 24;12:7799-7813. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S146978. eCollection 2017. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017. PMID: 29123394 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hideharu M, Mizuki I, Satoko I, Takeshi E. Ring-opening polymerization of γ-benzyl-l-glutamate-N-carboxyanhydride in ionic liquids. Polymer. 2007;48(20):5867–5877.
-
- Poché DS, Moore MJ, Bowles JL. An unconventional method for purifying the Ncarboxyanhydride derivatives of γ-alkyl-l-glutamates. Synth Commun. 1999;29(5):843–854.
-
- Zhuang W, Liao L, Chen H, Wang J, Pan Y, Zhang L, et al. Water-soluble star-block copolypeptides: towards biodegradable nanocarriers for versatile and simultaneous encapsulation. Macromol Rapid Commun. 2009;30:920–924. - PubMed
-
- Harada A, Kataoka K. Formation of polyion complex micelles in an aqueous milieu from a pair of oppositely-charged block copolymers with poly(ethylene glycol) segments. Macromolecules. 1995;28(15):5294–5299.
-
- Wu M, Ye Z, Liu Y, Liu B, Zhao X. Release of hydrophobic anticancer drug from a newly designed self-assembling peptide. Mol Biosyst. 2011;7(6):2040–2047. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

