Diagnostic value of BRAF (V600E)-mutation analysis in fine-needle aspiration of thyroid nodules: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 27175084
- PMCID: PMC4854268
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S101800
Diagnostic value of BRAF (V600E)-mutation analysis in fine-needle aspiration of thyroid nodules: a meta-analysis
Abstract
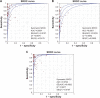
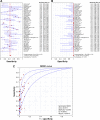
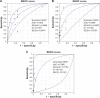
Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) is a reliable method for preoperative diagnosis of thyroid nodules; however, about 10%-40% nodules are classified as indeterminate. The BRAF (V600E) mutation is the most promising marker for thyroid FNA. This meta-analysis was conducted to investigate the diagnostic value of BRAF (V600E) analysis in thyroid FNA, especially the indeterminate cases. Systematic searches were performed in PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, Ovid, Elsevier, and the Cochrane Library databases for relevant studies prior to June 2015, and a total of 88 studies were ultimately included in this meta-analysis. Compared with FNA cytology, the synergism of BRAF (V600E) testing increased the diagnostic sensitivity from 81.4% to 87.4% and decreased the false-negative rate from 8% to 5.2%. In the indeterminate group, the mutation rate of BRAF (V600E) was 23% and varied in different subcategories (43.2% in suspicious for malignant cells [SMC], 13.77% in atypia of undetermined significance/follicular lesion of undetermined significance [AUS/FLUS], and 4.43% in follicular neoplasm/suspicious for follicular neoplasm [FN/SFN]). The sensitivity of BRAF (V600E) analysis was higher in SMC than that in AUS/FLUS and FN/SFN cases (59.4% vs 40.1% vs 19.5% respectively), while specificity was opposite (86.1% vs 99.5% vs 99.7% respectively). The areas under the summary receiver-operating characteristic curve also confirmed the diagnostic value of BRAF (V600E) testing in SMC and AUS/FLUS rather than FN/SFN cases. Therefore, BRAF (V600E) analysis can improve the diagnostic accuracy of thyroid FNA, especially indeterminate cases classified as SMC, and select malignancy to guide the extent of surgery.
Keywords: BRAFV600E mutation; fine-needle aspiration; meta-analysis; thyroid cancer.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Combined Use of Fine-Needle Aspiration (FNA) and BRAF V600E Gene Testing: Can it Increase the Definitive Diagnosis Rate of Nodules Categorized as Bethesda III for Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma?Am Surg. 2024 Dec;90(12):3209-3215. doi: 10.1177/00031348241265143. Epub 2024 Jul 24. Am Surg. 2024. PMID: 39047144
-
[Diagnostic Value of American Thyroid Association Guidelines,American College of Radiology Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System,and Chinese Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System Alone and Combined With BRAFV600E Mutation in Atypia of Undetermined Significance/Follicular Lesion of Undetermined Significance].Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2023 Dec 30;45(6):921-928. doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.15754. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2023. PMID: 38173102 Chinese.
-
Outcome of thyroid nodules characterized as atypia of undetermined significance or follicular lesion of undetermined significance and correlation with Ultrasound features and BRAF(V600E) mutation analysis.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2013 Dec;201(6):W854-60. doi: 10.2214/AJR.12.9901. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2013. PMID: 24261392
-
Testing for BRAF (V600E) Mutation in Thyroid Nodules with Fine-Needle Aspiration (FNA) Read as Suspicious for Malignancy (Bethesda V, Thy4, TIR4): a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Endocr Pathol. 2020 Mar;31(1):57-66. doi: 10.1007/s12022-019-09596-z. Endocr Pathol. 2020. PMID: 31811566
-
Follow-up of atypia and follicular lesions of undetermined significance in thyroid fine needle aspiration cytology.Cytopathology. 2013 Dec;24(6):385-90. doi: 10.1111/cyt.12021. Epub 2012 Oct 18. Cytopathology. 2013. PMID: 23078633 Review.
Cited by
-
Plasma Metabolic Profiling of Human Thyroid Nodules by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS)-Based Untargeted Metabolomics.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Jun 16;8:385. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00385. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32612989 Free PMC article.
-
BRAF mutation in cytologically indeterminate thyroid nodules: after reclassification of a variant thyroid carcinoma.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 Feb 21;12:1465-1473. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S190001. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 30863114 Free PMC article.
-
Lessons learned from the first 2 years of experience with thyroid core needle biopsy at an Indonesian national referral hospital.J Pathol Transl Med. 2025 May;59(3):149-160. doi: 10.4132/jptm.2025.02.19. Epub 2025 Apr 25. J Pathol Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40468609 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in metabolomics of thyroid cancer diagnosis and metabolic regulation.Endocrine. 2019 Jul;65(1):1-14. doi: 10.1007/s12020-019-01904-1. Epub 2019 Apr 1. Endocrine. 2019. PMID: 30937722 Review.
-
Association of telomerase reverse transcriptase promoter mutations with clinicopathological features and prognosis of thyroid cancer: a meta-analysis.Onco Targets Ther. 2016 Nov 11;9:6965-6976. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S116594. eCollection 2016. Onco Targets Ther. 2016. PMID: 27956840 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64(1):9–29. - PubMed
-
- Markovina S, Grigsby PW, Schwarz JK, et al. Treatment approach, surveillance, and outcome of well-differentiated thyroid cancer in childhood and adolescence. Thyroid. 2014;24(7):1121–1126. - PubMed
-
- Bongiovanni M, Krane JF, Cibas ES, Faquin WC. The atypical thyroid fine-needle aspiration: past, present, and future. Cancer Cytopathol. 2012;120(2):73–86. - PubMed
-
- Faquin WC, Bongiovanni M, Sadow PM. Update in thyroid fine needle aspiration. Endocr Pathol. 2011;22(4):178–183. - PubMed
-
- Seningen JL, Nassar A, Henry MR. Correlation of thyroid nodule fine-needle aspiration cytology with corresponding histology at Mayo Clinic, 2001–2007: an institutional experience of 1,945 cases. Diagn Cytopathol. 2012;40(Suppl 1):E27–E32. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

