First isolation of Mycobacterium spp. in Mullus spp. in Turkey
- PMID: 27175166
- PMCID: PMC4827678
First isolation of Mycobacterium spp. in Mullus spp. in Turkey
Abstract
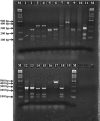
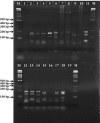
Ichthyozoonotic Mycobacterium spp. poses health risks both to fish and humans. In this study, the presence of ichthyozoonotic Mycobacterium spp. was investigated in red mullet (Mullus barbatus barbatus) and surmullet (Mullus surmuletus), widely caught species in the Mediterranean and the Aegean Sea. A total of 208 fish samples, provided from fishermen of Mersin province (Turkey) were studied. Using conventional methods, Mycobacterium spp. was isolated and identified at the genus level by PCR and at the species level by PCR-RFLP. Thirteen Mycobacterium spp. were detected in 13 (6.25%) fish samples. Four mycobacteria were identified as M. genavense, three as M. fortuitum, three as M. scrofulaceum, one as M. marinum, one as M. vaccae and one as M. aurum. No signs of mycobacteriosis were observed in fish samples. Findings of this study can contribute to future studies of onichthyozoonotic Mycobacterium spp. in seafood.
Keywords: Fish disease; Food safety; Mycobacterium spp.; Red mullet (Mullus barbatus barbatus); Surmullet (Mullus surmuletus).
Figures




Similar articles
-
RFLP analysis of mitochondrial DNA to evaluate genetic variation in striped red mullet (Mullus surmuletus L.) and red mullet (Mullus barbatus L.) populations.Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2001 May;3(3):264-74. doi: 10.1007/s101260000075. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2001. PMID: 14961364
-
An Epidemiological Update on Anisakis Nematode Larvae in Red Mullet (Mullus barbatus) from the Ligurian Sea.Pathogens. 2023 Nov 18;12(11):1366. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12111366. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 38003830 Free PMC article.
-
Mullus barbatus L. and Mullus surmuletus L. from western Mediterranean waters (SE Spain) are infected by Hysterothylacium fabri, but not by zoonotic nematodes. Possible impact on fish hosts.J Fish Dis. 2024 Oct;47(10):e13989. doi: 10.1111/jfd.13989. Epub 2024 Jul 2. J Fish Dis. 2024. PMID: 38957033
-
General characteristics, features of cultivation and antibiotic resistance representatives of mycobacterium fortuitum group representatives (review of literature).Klin Lab Diagn. 2021 Apr 17;66(4):223-228. doi: 10.51620/0869-2084-2021-66-4-223-228. Klin Lab Diagn. 2021. PMID: 33878244 Review. English.
-
Mycobacterial infections in domestic and wild animals due to Mycobacterium marinum, M. fortuitum, M. chelonae, M. porcinum, M. farcinogenes, M. smegmatis, M. scrofulaceum, M. xenopi, M. kansasii, M. simiae and M. genavense.Rev Sci Tech. 2001 Apr;20(1):265-90. doi: 10.20506/rst.20.1.1269. Rev Sci Tech. 2001. PMID: 11288516 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Identification and Characterization of Vibrio Species and Mycobacterium Species in Wild and Cultured Marine Fish from the Eastern Mediterranean Sea.Microorganisms. 2020 Jun 7;8(6):863. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8060863. Microorganisms. 2020. PMID: 32517374 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anonymous . Turkish Public Health Agency. Refik Saydam Hygiene Center; 2009. [(01.06.2009)]. Bacteriological diagnosis of tuberculosis. http://www.rshm.gov.tr.
-
- Austin, B, Austin, DA. Bacterial fish pathogens. 4th Edn. Chichester: Springer-Praxis; 2007. p. 552.
-
- Bercovier, H, Vincent, V. Mycobacterial infections in domestic and wild animals due to Mycobacterium marinum, M fortuitum, M. chelonae, M. porcinum, M. farcinogenes, M. smegmatis, M. scrofulaceum, M. xenopi, M. kansasii, M. simiae and M. genavense. Rev. Sci. Technol. 2001;20:265–290. - PubMed
-
- Decostere, A, Hermans, K, Haesebrouck, F. Piscine mycobacteriosis: a literature review covering the agent and the disease it causes in fish and humans. Vet. Microbiol. 2004;99:159–166. - PubMed
-
- Diamant, A, Banet, A, Ucko, M, Colorni, A, Knibb, W, Kvitt, H. Mycobacteriosis in wild rabbitfish, Siganus rivulatus, associated with cage farming in the Gulf of Eilat, Red Sea. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2000;39:211–219. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
