Targeting oncomiRNAs and mimicking tumor suppressor miRNAs: Νew trends in the development of miRNA therapeutic strategies in oncology (Review)
- PMID: 27175518
- PMCID: PMC4902075
- DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2016.3503
Targeting oncomiRNAs and mimicking tumor suppressor miRNAs: Νew trends in the development of miRNA therapeutic strategies in oncology (Review)
Abstract
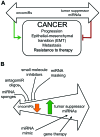
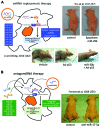
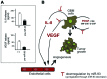
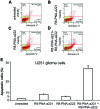
MicroRNA (miRNA or miR) therapeutics in cancer are based on targeting or mimicking miRNAs involved in cancer onset, progression, angiogenesis, epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis. Several studies conclusively have demonstrated that miRNAs are deeply involved in tumor onset and progression, either behaving as tumor-promoting miRNAs (oncomiRNAs and metastamiRNAs) or as tumor suppressor miRNAs. This review focuses on the most promising examples potentially leading to the development of anticancer, miRNA-based therapeutic protocols. The inhibition of miRNA activity can be readily achieved by the use of miRNA inhibitors and oligomers, including RNA, DNA and DNA analogues (miRNA antisense therapy), small molecule inhibitors, miRNA sponges or through miRNA masking. On the contrary, the enhancement of miRNA function (miRNA replacement therapy) can be achieved by the use of modified miRNA mimetics, such as plasmid or lentiviral vectors carrying miRNA sequences. Combination strategies have been recently developed based on the observation that i) the combined administration of different antagomiR molecules induces greater antitumor effects and ii) some anti-miR molecules can sensitize drug-resistant tumor cell lines to therapeutic drugs. In this review, we discuss two additional issues: i) the combination of miRNA replacement therapy with drug administration and ii) the combination of antagomiR and miRNA replacement therapy. One of the solid results emerging from different independent studies is that miRNA replacement therapy can enhance the antitumor effects of the antitumor drugs. The second important conclusion of the reviewed studies is that the combination of anti-miRNA and miRNA replacement strategies may lead to excellent results, in terms of antitumor effects.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The potential of miRNAs for diagnosis, treatment and monitoring of breast cancer.Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 2016;245:S34-9. doi: 10.1080/00365513.2016.1208444. Epub 2016 Jul 19. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 2016. PMID: 27435502 Review.
-
MicroRNA-based therapy and breast cancer: A comprehensive review of novel therapeutic strategies from diagnosis to treatment.Pharmacol Res. 2015 Jul;97:104-21. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2015.04.015. Epub 2015 May 7. Pharmacol Res. 2015. PMID: 25958353 Review.
-
Therapeutic potential of antagomiRs in haematological and oncological neoplasms.Eur J Cancer Care (Engl). 2020 Mar;29(2):e13208. doi: 10.1111/ecc.13208. Epub 2020 Jan 3. Eur J Cancer Care (Engl). 2020. PMID: 31899849 Review.
-
The therapeutic potential of microRNAs in cancer.Cancer J. 2012 May-Jun;18(3):275-84. doi: 10.1097/PPO.0b013e318258b5d6. Cancer J. 2012. PMID: 22647365
-
Small molecules targeting microRNA for cancer therapy: Promises and obstacles.J Control Release. 2015 Dec 10;219:237-247. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.08.011. Epub 2015 Aug 6. J Control Release. 2015. PMID: 26256260 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clear Cell Renal Carcinoma: MicroRNAs With Efficacy in Preclinical In Vivo Models.Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2021 May-Jun;18(3 Suppl):349-368. doi: 10.21873/cgp.20265. Epub 2021 May 15. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2021. PMID: 33994361 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of potential microRNA diagnostic panels and uncovering regulatory mechanisms in breast cancer pathogenesis.Sci Rep. 2022 Nov 22;12(1):20135. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-24347-7. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36418345 Free PMC article.
-
Biological role and clinical value of miR-99a-5p in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC): A bioinformatics-based study.FEBS Open Bio. 2018 Jun 26;8(8):1280-1298. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.12478. eCollection 2018 Aug. FEBS Open Bio. 2018. PMID: 30087832 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA nanoencapsulation to regulate the programming of the blood-brain barrier permeability by hypoxia.Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2022 Sep 15;3:100129. doi: 10.1016/j.crphar.2022.100129. eCollection 2022. Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2022. PMID: 36568262 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-643 promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis of papillary thyroid carcinoma by down-regulating the cytochrome P450 family member 11B1.Transl Cancer Res. 2020 Mar;9(3):1465-1475. doi: 10.21037/tcr.2020.01.43. Transl Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 35117494 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Krol J, Loedige I, Filipowicz W. The widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay. Nat Rev Genet. 2010;11:597–610. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

