Estrogen regulates miRNA expression: implication of estrogen receptor and miR-124/AKT2 in tumor growth and angiogenesis
- PMID: 27175587
- PMCID: PMC5095050
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.9230
Estrogen regulates miRNA expression: implication of estrogen receptor and miR-124/AKT2 in tumor growth and angiogenesis
Abstract
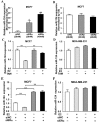
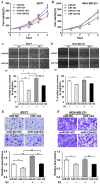
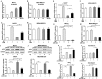
It is currently known that estrogen plays an important role in breast cancer (BC) development, but the underlying molecular mechanism remains to be elucidated. Accumulating evidence has revealed important roles of microRNAs in various kinds of human cancers, including BC. In this study, we found that among the microRNAs regulated by estrogen, miR-124 was the most prominent downregulated miRNA. miR-124 was downregulated by estradiol (E2) treatment in estrogen receptor (ER) positive BC cells, miR-124 overexpression suppressed cell proliferation, migration and invasion in BC cells; while the suppression of miR-124 using Anti-miR-124 inhibitor had opposite cellular functions. Under the E2 treatment, miR-124 had stronger effect to inhibit cellular functions in MCF7 cells than that in MDA-MB-231 cells. In addition, we identified that ERα, but not ERβ, was required for E2-induced miR-124 downregulation. Furthermore, AKT2, a known oncogene, was a novel direct target of miR-124. AKT2 expression levels were inversely correlated with miR-124 expression levels in human breast cancer specimens. AKT2 was overexpressed in BC specimens, and its expression levels were much higher in ERα positive cancer tissues than those ERα negative cancer tissues. Consistent with miR-124 suppression, E2 treatment increased AKT2 expression levels in MCF7 cells via ERα. Finally, overexpression of miR-124 in MCF7 cells significantly suppressed tumor growth and angiogenesis by targeting AKT2. Our results provide a mechanistic insight into a functional role of new ERα/miR-124/AKT2 signaling pathway in BC development. miR-124 and AKT2 may be used as biomarkers for ERα positive BC and therapeutic effect in the future.
Keywords: AKT2; breast cancer; estrogen; estrogen receptors; miR-124.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Overexpression of microRNA-190 inhibits migration, invasion, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and angiogenesis through suppression of protein kinase B-extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathway via binding to stanniocalicin 2 in breast cancer.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Aug;234(10):17824-17838. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28409. Epub 2019 Apr 16. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30993707
-
miR-191/DAB2 axis regulates the tumorigenicity of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer.IUBMB Life. 2018 Jan;70(1):71-80. doi: 10.1002/iub.1705. Epub 2017 Dec 16. IUBMB Life. 2018. PMID: 29247596
-
Estrogen receptor beta as epigenetic mediator of miR-10b and miR-145 in mammary cancer.Matrix Biol. 2017 Dec;64:94-111. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2017.08.002. Epub 2017 Aug 8. Matrix Biol. 2017. PMID: 28797712
-
Anti-miR-203 suppresses ER-positive breast cancer growth and stemness by targeting SOCS3.Oncotarget. 2016 Sep 6;7(36):58595-58605. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11193. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27517632 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estrogen receptor alpha phosphorylation and its functional impact in human breast cancer.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015 Dec 15;418 Pt 3:264-72. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2015.01.016. Epub 2015 Jan 15. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 25597633 Review.
Cited by
-
Estradiol Downregulates MicroRNA-193a to Mediate Its Anti-Mitogenic Actions on Human Coronary Artery Smooth Muscle Cell Growth.Cells. 2025 Jul 23;14(15):1132. doi: 10.3390/cells14151132. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40801565 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomal miR-665 as a novel minimally invasive biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis and prognosis.Oncotarget. 2017 Sep 14;8(46):80666-80678. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20881. eCollection 2017 Oct 6. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29113334 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of MicroRNA-497-Targeting AKT2 Influences Tumor Growth and Chemoresistance to Cisplatin in Lung Cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Sep 8;8:840. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00840. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33015042 Free PMC article.
-
The regulatory role of microRNAs in angiogenesis-related diseases.J Cell Mol Med. 2018 Oct;22(10):4568-4587. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13700. Epub 2018 Jun 29. J Cell Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29956461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA Regulation of Breast Cancer Stemness.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 4;22(7):3756. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073756. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33916548 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pinho FG, Frampton AE, Nunes J, Krell J, Alshaker H, Jacob J, Pellegrino L, Roca-Alonso L, de Giorgio A, Harding V, Waxman J, Stebbing J, Pchejetski D, Castellano L. Downregulation of microRNA-515-5p by the estrogen receptor modulates sphingosine kinase 1 and breast cancer cell proliferation. Cancer research. 2013;73:5936–5948. - PubMed
-
- Clemons M, Goss P. Estrogen and the risk of breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:276–285. - PubMed
-
- Yager JD, Davidson NE. Estrogen carcinogenesis in breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:270–282. - PubMed
-
- Sommer S, Fuqua SA. Estrogen receptor and breast cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 2001;11:339–352. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

