The wiring diagram of a glomerular olfactory system
- PMID: 27177418
- PMCID: PMC4930330
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.14859
The wiring diagram of a glomerular olfactory system
Abstract
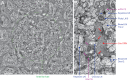
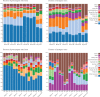
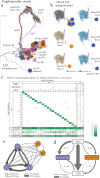
The sense of smell enables animals to react to long-distance cues according to learned and innate valences. Here, we have mapped with electron microscopy the complete wiring diagram of the Drosophila larval antennal lobe, an olfactory neuropil similar to the vertebrate olfactory bulb. We found a canonical circuit with uniglomerular projection neurons (uPNs) relaying gain-controlled ORN activity to the mushroom body and the lateral horn. A second, parallel circuit with multiglomerular projection neurons (mPNs) and hierarchically connected local neurons (LNs) selectively integrates multiple ORN signals already at the first synapse. LN-LN synaptic connections putatively implement a bistable gain control mechanism that either computes odor saliency through panglomerular inhibition, or allows some glomeruli to respond to faint aversive odors in the presence of strong appetitive odors. This complete wiring diagram will support experimental and theoretical studies towards bridging the gap between circuits and behavior.
Keywords: D. melanogaster; Drosophila; connectomics; electron microscopy; neural circuits; neuroscience; olfaction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures












References
-
- Bellmann D, Richardt A, Freyberger R, Nuwal N, Schwärzel M, Fiala A, Störtkuhl KF. Optogenetically Induced Olfactory Stimulation in Drosophila Larvae Reveals the Neuronal Basis of Odor-Aversion behavior. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience. 2010;4:e14859. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2010.00027. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

