Voluntary Running-Wheel Activity, Arterial Blood Gases, and Thermal Antinociception in Rats after 3 Buprenorphine Formulations
- PMID: 27177564
- PMCID: PMC4865692
Voluntary Running-Wheel Activity, Arterial Blood Gases, and Thermal Antinociception in Rats after 3 Buprenorphine Formulations
Abstract
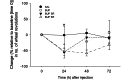
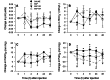
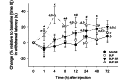
Buprenorphine HCl (BUP) is a μ-opioid agonist used in laboratory rodents. New formulations of buprenorphine (for example, sustained-released buprenorphine [BUP SR], extended-release buprenorphine [BUP ER]) have been developed to extend the analgesic duration. In a crossover design, 8 adult rats were injected subcutaneously with either BUP, BUP SR, BUP ER, or saline, after which voluntary running-wheel activity, arterial blood gases, and thermal withdrawal latency were assessed. Wheel running was decreased at 24 h compared with baseline in all treatment groups but returned to baseline by 48 h. Arterial pH, HCO3(-), and CO2 were not changed between groups or over time. However, arterial oxygen was lower than baseline in the BUP (-8 ± 2 mm Hg), BUP SR (-7 ± 1 mm Hg), and BUP ER (-17 ± 2 mm Hg) groups compared with saline controls (3 ± 2 mm Hg); the BUP ER group showed the greatest decrease when all time points were combined. BUP increased the withdrawal latency at 1 h (15% ± 3%), whereas BUP ER increased latencies at 4, 8, 12, and 48 h (35% ± 11%, 21% ± 7%, 26% ± 7%, and 22% ± 9%, respectively) and BUP SR prolonged latencies at 24, 48, and 72 h (15% ± 6%, 18% ± 5%, and 20% ± 8%, respectively). The duration of thermal analgesia varied between buprenorphine formulations, but all 3 formulations reduced voluntary-running activity at 24 h after injection and might cause hypoxemia in normal adult rats.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of Sustained-Release Buprenorphine in an Experimental Laparotomy Model in Female Mice.J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2016 Jan;55(1):66-73. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2016. PMID: 26817982 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetics and Paw Withdrawal Pressure in Female Guinea Pigs (Cavia porcellus) Treated with Sustained-Release Buprenorphine and Buprenorphine Hydrochloride.J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2016 Nov;55(6):789-793. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2016. PMID: 27931318 Free PMC article.
-
Antinociceptive effects of sustained-release buprenorphine in a model of incisional pain in rats (Rattus norvegicus).J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2014 Mar;53(2):193-7. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2014. PMID: 24602547 Free PMC article.
-
Buprenorphine treatment for opioid use disorder: recent progress.Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2019 Aug;12(8):791-803. doi: 10.1080/17512433.2019.1635454. Epub 2019 Jun 30. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31232604 Review.
-
Opioids and the management of chronic severe pain in the elderly: consensus statement of an International Expert Panel with focus on the six clinically most often used World Health Organization Step III opioids (buprenorphine, fentanyl, hydromorphone, methadone, morphine, oxycodone).Pain Pract. 2008 Jul-Aug;8(4):287-313. doi: 10.1111/j.1533-2500.2008.00204.x. Epub 2008 May 23. Pain Pract. 2008. PMID: 18503626
Cited by
-
Lack of Absorption of a Sustained-release Buprenorphine Formulation Administered Subcutaneously to Athymic Nude Rats.J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2019 Sep 1;58(5):597-600. doi: 10.30802/AALAS-JAALAS-19-000013. Epub 2019 Jul 30. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2019. PMID: 31362805 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk between bone metastatic cancer cells and sensory nerves in bone metastatic progression.Life Sci Alliance. 2024 Sep 12;7(12):e202302041. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202302041. Print 2024 Dec. Life Sci Alliance. 2024. PMID: 39266299 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Management of Pain in Rodents.Comp Med. 2019 Dec 1;69(6):468-489. doi: 10.30802/AALAS-CM-19-000048. Epub 2019 Dec 10. Comp Med. 2019. PMID: 31822323 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Side effects of pain and analgesia in animal experimentation.Lab Anim (NY). 2017 Mar 22;46(4):123-128. doi: 10.1038/laban.1216. Lab Anim (NY). 2017. PMID: 28328895 Review.
-
Design and in vivo evaluation of a microparticulate depot formulation of buprenorphine for veterinary use.Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 14;10(1):17295. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-74230-6. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33057103 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Animalgesic Labs. [Internet]. 2015. Studies–Animalgesics. [Cited 06 August 2015] Available at: www.animalgesiclabs.com
-
- Brun-Pascaud M, Gaudebout C, Blayo MC, Pocidalo JJ. 1982. Arterial blood gases and acid-base status in awake rats. Respir Physiol 48:45–57. - PubMed
-
- Christoph T, Kögel B, Schiene K, Méen M, De Vry J, Friderichs E. 2005. Broad analgesic profile of buprenorphine in rodent models of acute and chronic pain. Eur J Pharmacol 507:87–98. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
