Speckle tracking echocardiography in patients with septic shock: a case control study (SPECKSS)
- PMID: 27177587
- PMCID: PMC4867983
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-016-1327-0
Speckle tracking echocardiography in patients with septic shock: a case control study (SPECKSS)
Abstract
Background: Sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction is a well-recognized condition and confers worse outcomes in septic patients. Echocardiographic assessment by conventional parameters such as left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is often affected by ongoing changes in preload and afterload conditions. Novel echocardiographic technologies such as speckle tracking echocardiography (STE) have evolved for direct assessment of the myocardial function. We investigate the measurement of myocardial strain by speckle tracking echocardiography for the diagnosis of sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction.
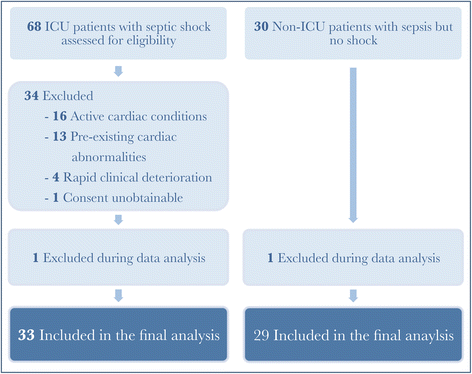
Methods: This is a case-control study at a university-affiliated medical intensive care unit. Consecutive adult medical patients admitted with a diagnosis of septic shock were included. Patients with other causes of myocardial dysfunction were excluded. They were compared to age-matched, gender-matched, and cardiovascular risk-factor-matched controls, who were admitted to hospital for sepsis but did not develop septic shock. Transthoracic echocardiography was performed on all patients within 24 hours of diagnosis, and a reassessment echocardiogram was performed in the study group of patients upon recovery.
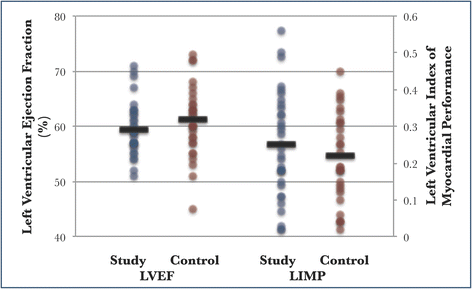
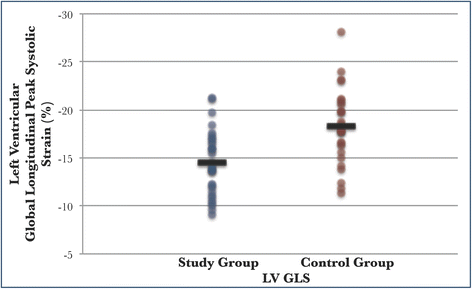
Results: Patients with septic shock (n = 33) (study group) and 29 matched patients with sepsis but no septic shock (control group) were recruited. The mean sequential organ failure assessment (SOFA) score for the study and control groups were 10.2 and 1.6, respectively (P < 0.001). In patients with septic shock, the mean arterial pressure was lower (76 mmHg vs 82 mmHg, P = 0.032), and the heart rate was higher (99 bpm vs 86 bpm, P = 0.008). The cardiac output (5.9 L/min vs 5.5 L/min, P = 0.401) and systemic vascular resistance (1090 dynes•sec/cm(5) vs 1194 dynes•sec/cm(5), P = 0.303) were similar. The study group had a greater degree of myocardial dysfunction measured by global longitudinal strain (GLS) (-14.5 % vs -18.3 %, P <0.001), and the myocardial strain differed upon diagnosis and recovery (-14.5 % vs -16.0 %, P = 0.010). Conventional echocardiographic measurements such as LVEF (59 % in the study group vs 61 % in the control group, P = 0.169) did not differ between the two groups.
Conclusion: Speckle tracking echocardiography can detect significant left ventricular impairment in patients with septic shock, which was not otherwise detectable by conventional echocardiography. The reversible nature of myocardial dysfunction in sepsis was also demonstrable. This echocardiographic technique is useful in the diagnosis and monitoring of sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction.
Keywords: Global longitudinal strain; Sepsis; Sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction; Septic cardiomyopathy; Septic shock; Speckle tracking echocardiography; Speckle tracking imaging; Strain.
Figures
Comment in
-
Speckle tracking echocardiography: another step towards early detection of septic myocardial dysfunction?Crit Care. 2016 Aug 18;20(1):236. doi: 10.1186/s13054-016-1411-5. Crit Care. 2016. PMID: 27535825 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The role of speckle tracking echocardiography for prognostication in patients with severe sepsis or septic shock.Crit Care. 2016 Sep 12;20(1):284. doi: 10.1186/s13054-016-1451-x. Crit Care. 2016. PMID: 27616201 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Strain echocardiography identifies impaired longitudinal systolic function in patients with septic shock and preserved ejection fraction.Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2015 Jul 2;13:30. doi: 10.1186/s12947-015-0025-4. Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2015. PMID: 26134971 Free PMC article.
-
Subclinical Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction in Patients with Septic Shock Based on Sepsis-3 Definition: A Speckle-Tracking Echocardiography Study.Crit Care Res Pract. 2020 Sep 21;2020:6098654. doi: 10.1155/2020/6098654. eCollection 2020. Crit Care Res Pract. 2020. PMID: 33014463 Free PMC article.
-
Two-dimensional speckle tracking imaging detects impaired myocardial performance in children with septic shock, not recognized by conventional echocardiography.Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2012 May;13(3):259-64. doi: 10.1097/PCC.0b013e3182288445. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2012. PMID: 21760563
-
Left ventricular systolic function evaluated by strain echocardiography and relationship with mortality in patients with severe sepsis or septic shock: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Crit Care. 2018 Aug 4;22(1):183. doi: 10.1186/s13054-018-2113-y. Crit Care. 2018. PMID: 30075792 Free PMC article.
-
Global Longitudinal Strain Using Speckle-Tracking Echocardiography as a Mortality Predictor in Sepsis: A Systematic Review.J Intensive Care Med. 2019 Feb;34(2):87-93. doi: 10.1177/0885066618761750. Epub 2018 Mar 18. J Intensive Care Med. 2019. PMID: 29552957
Cited by
-
The role of speckle tracking echocardiography for prognostication in patients with severe sepsis or septic shock.Crit Care. 2016 Sep 12;20(1):284. doi: 10.1186/s13054-016-1451-x. Crit Care. 2016. PMID: 27616201 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Use of speckle-tracking strain in preload-dependent patients, need for cautious interpretation!Ann Intensive Care. 2018 Feb 21;8(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s13613-018-0376-8. Ann Intensive Care. 2018. PMID: 29468335 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical implications of septic cardiomyopathy: A narrative review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Apr 26;103(17):e37940. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000037940. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38669408 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic Role of Left Ventricular Systolic Function Measured by Speckle Tracking Echocardiography in Septic Shock.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Oct 21;2020:7927353. doi: 10.1155/2020/7927353. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 33150180 Free PMC article.
-
Right ventricular strain measurements in critically ill patients: an observational SICS sub-study.Ann Intensive Care. 2022 Oct 3;12(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s13613-022-01064-y. Ann Intensive Care. 2022. PMID: 36190597 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tei C, Ling LH, Hodge DO, Bailey KR, Oh JK, Rodeheffer RJ, et al. New index of combined systolic and diastolic myocardial performance: a simple and reproducible measure of cardiac function--a study in normals and dilated cardiomyopathy. J Cardiol. 1995;26(6):357–366. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

