Hydatid cyst fluid promotes peri-cystic fibrosis in cystic echinococcosis by suppressing miR-19 expression
- PMID: 27177776
- PMCID: PMC4866024
- DOI: 10.1186/s13071-016-1562-x
Hydatid cyst fluid promotes peri-cystic fibrosis in cystic echinococcosis by suppressing miR-19 expression
Abstract
Background: Echinococcus granulosus infection causes cystic echinococcosis (CE); the generation of liver fibrosis around the parasitic larval cyst (metacestode) may play a major role in the spontaneous limitation of the parasitic growth; however, fibrogenesis has received little attention in CE. It has been reported that miR-19b plays a role in various diseases, including infectious diseases, by regulating fibrogenesis. However, its function in the development of liver fibrosis in E. granulosus infection is unknown.
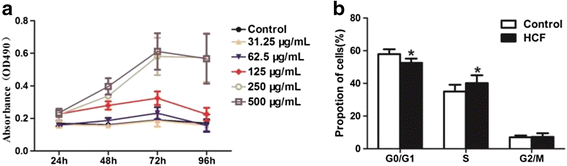
Methods: The expression of miR-19b and genes that are involved in liver fibrosis were analysed in E. granulosus-infected human livers using qRT-PCR. The role of miR-19b on hepatic stellate cells (LX-2 cells in vitro) treated with hydatid cyst fluid (HCF) was then analysed by 3-(4, 5-dimet-hylthiazol-2-yl)-2, 4-diphenyl-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay, qRT-PCR, Western blot and flow cytometry.
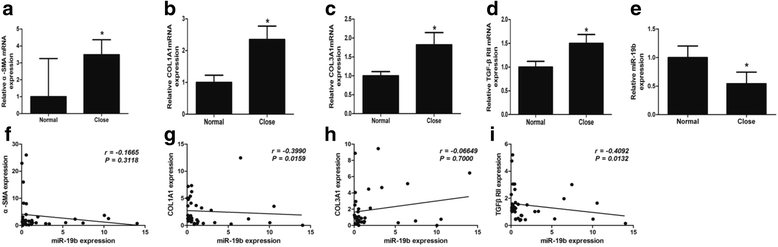
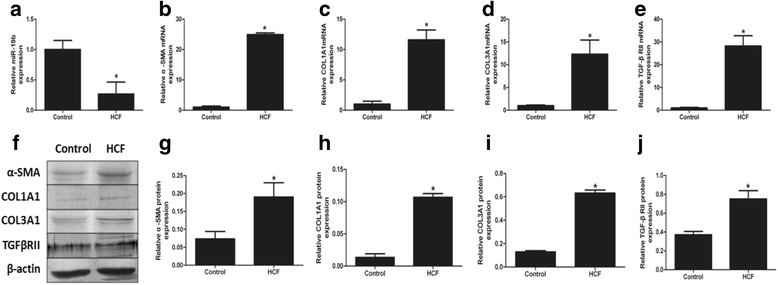
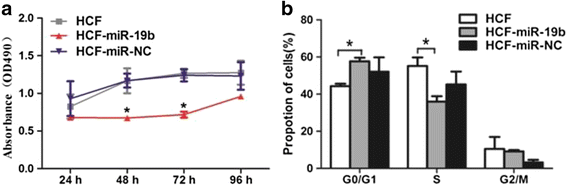
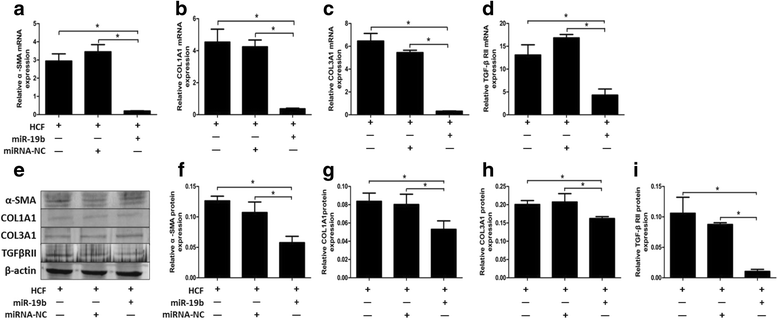
Results: The results showed that the expression of miR-19 was significantly reduced in the pericystic collagen-rich liver tissue of CE patients, compared to normal liver. Incubation of LX-2 cells (in vitro) with HCF induced a decreased proliferation of these cells and a reduced expression of miR-19, inversely correlated with the expression of collagen 1A1 and TGF-β receptor II (TβRII). Conversely, overexpression of miR-19 by LX-2 cells inhibited the proliferation of these cells and led to decreased TβRII expression.
Conclusions: Our study provides new evidence for the intervention of miRNAs in the regulation of fibrosis in infectious diseases; it suggests that E. granulosus can inhibit miR-19 liver expression and promote fibrosis through the increase in TβRII, the activation of hepatic stellate cells and extracellular matrix production.
Keywords: Echinococcus granulosus; HSC; Liver fibrosis; TβRII; miR-19.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Effects of Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Hydatid Cyst Fluid on the Expression of microRNAs Involved in Liver Fibrosis.Acta Parasitol. 2025 Apr 12;70(2):89. doi: 10.1007/s11686-025-01024-z. Acta Parasitol. 2025. PMID: 40220059
-
Can Echinococcus granulosus-Derived MicroRNAs be Biomarkers for Diagnosis and Follow-up of Cystic Echinococcosis Patients?Acta Parasitol. 2023 Mar;68(1):231-239. doi: 10.1007/s11686-022-00654-x. Epub 2023 Jan 13. Acta Parasitol. 2023. PMID: 36637695
-
MicroRNA-19b reduces hepatic stellate cell proliferation by targeting GRB2 in hepatic fibrosis models in vivo and in vitro as part of the inhibitory effect of estradiol.J Cell Biochem. 2015 Nov;116(11):2455-64. doi: 10.1002/jcb.25116. J Cell Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25650006
-
Echinococcosis and allergy.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2004 Apr;26(2):93-104. doi: 10.1007/s12016-004-0004-2. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15146106 Review.
-
[Cystic echinococcosis in humans: our clinic experience].Parassitologia. 2004 Jun;46(1-2):45-51. Parassitologia. 2004. PMID: 15305685 Review. Italian.
Cited by
-
HLA class II profile in patients with different stages of cystic echinococcosis according to the WHO ultrasound imaging classification.Parasitol Res. 2024 Sep 24;123(9):330. doi: 10.1007/s00436-024-08353-4. Parasitol Res. 2024. PMID: 39316156
-
Echinococcus granulosus cyst fluid suppresses inflammatory responses by inhibiting TRAF6 signalling in macrophages.Parasitology. 2021 Jun;148(7):887-894. doi: 10.1017/S0031182021000548. Epub 2021 Mar 29. Parasitology. 2021. PMID: 33775265 Free PMC article.
-
A pilot study of microRNAs expression profile in plasma of patients with hydatid disease: potential immunomodulation of hydatid disease.Parasitol Res. 2024 Sep 30;123(10):336. doi: 10.1007/s00436-024-08350-7. Parasitol Res. 2024. PMID: 39347812
-
Mechanism of Fibrosis Induced by Echinococcus spp.Diseases. 2019 Aug 12;7(3):51. doi: 10.3390/diseases7030051. Diseases. 2019. PMID: 31409055 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miRNAs and lncRNAs in Echinococcus and Echinococcosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jan 22;21(3):730. doi: 10.3390/ijms21030730. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 31979099 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Peng XY, Wu XW, Zhang SJ, Niu JH. The new aspects in recognition of pathogenesis of the pericyst of human hepatic Echinococcus granulosus. World Chin J Digestol. 2005;13:276–9.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

