Enhanced incorporation of dietary DHA into lymph phospholipids by altering its molecular carrier
- PMID: 27178174
- PMCID: PMC4911702
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2016.05.002
Enhanced incorporation of dietary DHA into lymph phospholipids by altering its molecular carrier
Abstract
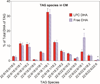
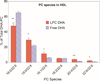
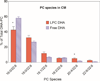
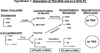
Several previous studies indicated that for optimal uptake by the brain, docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) should be present as phospholipid in the plasma. However most of dietary DHA is absorbed as triacylglycerol (TAG) because it is released as free fatty acid during digestion of either TAG-DHA (fish oil) or sn-2-DHA phospholipid (krill oil), and subsequently incorporated into TAG of chylomicrons. We tested the hypothesis that the absorption of DHA as phospholipid can be increased if it is present in the sn-1 position of dietary phospholipid or in lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC), because it would escape the hydrolysis by pancreatic phospholipase A2. We infused micelle containing the DHA either as LPC or as free acid, into the duodenum of lymph cannulated rats, and analyzed the chylomicrons and HDL of the lymph for the DHA-containing lipids. The results show that while the total amount of DHA absorbed was comparable from the two types of micelle, the percentage of DHA recovered in lymph phospholipids was 5 times greater with LPC-DHA, compared to free DHA. Furthermore, the amount of DHA recovered in lymph HDL was increased by 2-fold when LPC-DHA micelle was infused. These results could potentially lead to a novel strategy to increase brain DHA levels through the diet.
Keywords: Chylomicrons/HDL; Fish oil/DHA; Lymph; Lysophosphatidylcholine; Micelles; Phospholipids/absorption.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures






References
-
- Alessandri JM, Guesnet P, Vancassel S FAU - Astorg P, Astorg PF, Denis IF, Langelier BF, Aid S FAU - Poumes-Ballihaut C, Poumes-Ballihaut CF, Champeil-Potokar GF, Lavialle M. Polyunsaturated fatty acids in the central nervous system: evolution of concepts and nutritional implications throughout life. Reprod. Nutr Dev. 2004;44:509–538. - PubMed
-
- Chen CT, MA DWL, Kim JH, Mount HTJ, Bazinet RP. The low density lipoprotein receptor is not necessary for maintaining mouse brain polyunsaturated fatty acid concentrations. J. Lipid Res. 2008;49:147–152. - PubMed
-
- Rahman T, Taha AY, Jun Song B, Orr SK, Liu Z, Chen CT, Bazinet RP. The very low density lipoprotein receptor is not necessary for maintaining brain polyunsaturated fatty acid concentrations. Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes and Essential Fatty Acids. 2010;82:141–145. - PubMed
-
- Thies F, Pillon C, Moliere P, Lagarde M, Lecerf J. Preferential incorporation of sn-2 lysoPC DHA over unesterified DHA in the young rat brain. Amer. J. Physiol-Regul. Integr. C. 1994;36:R1273–R1279. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

