Regulation of CD44 expression and focal adhesion by Golgi phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate in breast cancer
- PMID: 27178239
- PMCID: PMC4946718
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.12968
Regulation of CD44 expression and focal adhesion by Golgi phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate in breast cancer
Abstract
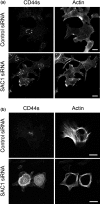
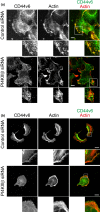
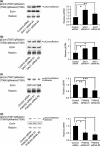
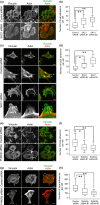
CD44, a transmembrane receptor, is expressed in the standard or variant form and plays a critical role in tumor progression and metastasis. This protein regulates cell adhesion and migration in breast cancer cells. We previously reported that phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate (PI(4)P) at the Golgi regulates cell migration and invasion in breast cancer cell lines. In this study, we showed that an increase in PI(4)P levels at the Golgi by knockdown of PI(4)P phosphatase SAC1 increased the expression of standard CD44, variant CD44, and ezrin/radixin phosphorylation and enhanced the formation of focal adhesions mediated by CD44 and ezrin/radixin in MCF7 and SK-BR-3 cells. In contrast, knockdown of PI 4-kinase IIIβ in highly invasive MDA-MB-231 cells decreased these factors. These results suggest that SAC1 expression and PI(4)P at the Golgi are important in tumor progression and metastasis and are potential prognostic markers of breast cancers.
Keywords: Breast cancer; CD44; SAC1; focal adhesion; phosphatidylinositol-4-monophosphate.
© 2016 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures



References
-
- Fox SB, Fawcett J, Jackson DG et al Normal human tissues, in addition to some tumors, express multiple different CD44 isoforms. Cancer Res 1994; 54: 4539–46. - PubMed
-
- Kaufmann M, Heider KH, Sinn HP, von Minckwitz G, Ponta H, Herrlich P. CD44 variant exon epitopes in primary breast cancer and length of survival. Lancet 1995; 345: 615–19. - PubMed
-
- Barshishat M, Ariel A, Cahalon L, Chowers Y, Lider O, Schwartz B. TNFalpha and IL‐8 regulate the expression and function of CD44 variant proteins in human colon carcinoma cells. Clin Exp Metastasis 2002; 19: 327–37. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

