ESR1 mutations affect anti-proliferative responses to tamoxifen through enhanced cross-talk with IGF signaling
- PMID: 27178332
- PMCID: PMC5510243
- DOI: 10.1007/s10549-016-3829-5
ESR1 mutations affect anti-proliferative responses to tamoxifen through enhanced cross-talk with IGF signaling
Erratum in
-
Erratum to: ESR1 mutations affect anti-proliferative responses to tamoxifen through enhanced cross-talk with IGF signaling.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2017 Jun;163(3):639-640. doi: 10.1007/s10549-017-4250-4. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2017. PMID: 28439737 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
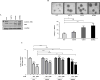
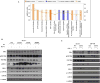
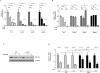
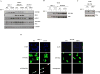
The purpose of this study was to address the role of ESR1 hormone-binding mutations in breast cancer. Soft agar anchorage-independent growth assay, Western blot, ERE reporter transactivation assay, proximity ligation assay (PLA), coimmunoprecipitation assay, silencing assay, digital droplet PCR (ddPCR), Kaplan-Meier analysis, and statistical analysis. It is now generally accepted that estrogen receptor (ESR1) mutations occur frequently in metastatic breast cancers; however, we do not yet know how to best treat these patients. We have modeled the three most frequent hormone-binding ESR1 (HBD-ESR1) mutations (Y537N, Y537S, and D538G) using stable lentiviral transduction in human breast cancer cell lines. Effects on growth were examined in response to hormonal and targeted agents, and mutation-specific changes were studied using microarray and Western blot analysis. We determined that the HBD-ESR1 mutations alter anti-proliferative effects to tamoxifen (Tam), due to cell-intrinsic changes in activation of the insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGF1R) signaling pathway and levels of PIK3R1/PIK3R3. The selective estrogen receptor degrader, fulvestrant, significantly reduced the anchorage-independent growth of ESR1 mutant-expressing cells, while combination treatments with the mTOR inhibitor everolimus, or an inhibitor blocking IGF1R, and the insulin receptor significantly enhanced anti-proliferative responses. Using digital drop (dd) PCR, we identified mutations at high frequencies ranging from 12 % for Y537N, 5 % for Y537S, and 2 % for D538G in archived primary breast tumors from women treated with adjuvant mono-tamoxifen therapy. The HBD-ESR1 mutations were not associated with recurrence-free or overall survival in response in this patient cohort and suggest that knowledge of other cell-intrinsic factors in combination with ESR1 mutation status will be needed determine anti-proliferative responses to Tam.
Keywords: Estrogen Receptor; Everolimus; Fulvestrant; IGF-1; Mutations.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors have nothing to disclose
Figures
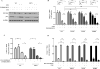
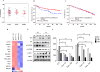
Similar articles
-
Upregulation of IRS1 Enhances IGF1 Response in Y537S and D538G ESR1 Mutant Breast Cancer Cells.Endocrinology. 2018 Jan 1;159(1):285-296. doi: 10.1210/en.2017-00693. Endocrinology. 2018. PMID: 29029116 Free PMC article.
-
The prevalence of estrogen receptor-1 mutation in advanced breast cancer: The estrogen receptor one study (EROS1).Cancer Treat Res Commun. 2019;19:100123. doi: 10.1016/j.ctarc.2019.100123. Epub 2019 Feb 21. Cancer Treat Res Commun. 2019. PMID: 30826563
-
The association between type of endocrine therapy and development of estrogen receptor-1 mutation(s) in patients with hormone-sensitive advanced breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized and non-randomized trials.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2019 Dec;1872(2):188315. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2019.188315. Epub 2019 Oct 21. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31647985
-
Longitudinal Molecular Imaging of Progesterone Receptor Reveals Early Differential Response to Endocrine Therapy in Breast Cancer with an Activating ESR1 Mutation.J Nucl Med. 2021 Apr;62(4):500-506. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.120.249508. Epub 2020 Aug 28. J Nucl Med. 2021. PMID: 32859700 Free PMC article.
-
ESR1 mutation as an emerging clinical biomarker in metastatic hormone receptor-positive breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2021 Aug 15;23(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s13058-021-01462-3. Breast Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34392831 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Notch Signaling Pathway and Endocrine Resistance in Breast Cancer.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Jun 19;11:924. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00924. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32636747 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Transcriptomic Analysis of the Pituitary Gland between Cattle Breeds Differing in Growth: Yunling Cattle and Leiqiong Cattle.Animals (Basel). 2020 Jul 25;10(8):1271. doi: 10.3390/ani10081271. Animals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32722439 Free PMC article.
-
CDK4/6 Inhibitors Overcome Endocrine ESR1 Mutation-Related Resistance in Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Feb 18;15(4):1306. doi: 10.3390/cancers15041306. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36831647 Free PMC article.
-
Personalized medicine in breast cancer: pharmacogenomics approaches.Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2019 May 27;12:59-73. doi: 10.2147/PGPM.S167886. eCollection 2019. Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2019. PMID: 31213877 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RON signalling promotes therapeutic resistance in ESR1 mutant breast cancer.Br J Cancer. 2021 Jan;124(1):191-206. doi: 10.1038/s41416-020-01174-z. Epub 2020 Dec 1. Br J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33257837 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tamoxifen for early breast cancer: an overview of the randomised trials. Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group. Lancet. 1998;351:1451–1467. - PubMed
-
- Johnston SR. New strategies in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research. 2010;16:1979–1987. - PubMed
-
- Jeselsohn R, Yelensky R, Buchwalter G, Frampton G, Meric-Bernstam F, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, et al. Emergence of constitutively active estrogen receptor-alpha mutations in pretreated advanced estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research. 2014;20:1757–1767. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Merenbakh-Lamin K, Ben-Baruch N, Yeheskel A, Dvir A, Soussan-Gutman L, Jeselsohn R, et al. D538G mutation in estrogen receptor-alpha: A novel mechanism for acquired endocrine resistance in breast cancer. Cancer research. 2013;73:6856–6864. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

