Abortion incidence between 1990 and 2014: global, regional, and subregional levels and trends
- PMID: 27179755
- PMCID: PMC5498988
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30380-4
Abortion incidence between 1990 and 2014: global, regional, and subregional levels and trends
Abstract
Background: Information about the incidence of induced abortion is needed to motivate and inform efforts to help women avoid unintended pregnancies and to monitor progress toward that end. We estimate subregional, regional, and global levels and trends in abortion incidence for 1990 to 2014, and abortion rates in subgroups of women. We use the results to estimate the proportion of pregnancies that end in abortion and examine whether abortion rates vary in countries grouped by the legal status of abortion.
Methods: We requested abortion data from government agencies and compiled data from international sources and nationally representative studies. With data for 1069 country-years, we estimated incidence using a Bayesian hierarchical time series model whereby the overall abortion rate is a function of the modelled rates in subgroups of women of reproductive age defined by their marital status and contraceptive need and use, and the sizes of these subgroups.
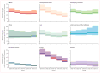
Findings: We estimated that 35 abortions (90% uncertainty interval [UI] 33 to 44) occurred annually per 1000 women aged 15-44 years worldwide in 2010-14, which was 5 points less than 40 (39-48) in 1990-94 (90% UI for decline -11 to 0). Because of population growth, the annual number of abortions worldwide increased by 5.9 million (90% UI -1.3 to 15.4), from 50.4 million in 1990-94 (48.6 to 59.9) to 56.3 million (52.4 to 70.0) in 2010-14. In the developed world, the abortion rate declined 19 points (-26 to -14), from 46 (41 to 59) to 27 (24 to 37). In the developing world, we found a non-significant 2 point decline (90% UI -9 to 4) in the rate from 39 (37 to 47) to 37 (34 to 46). Some 25% (90% UI 23 to 29) of pregnancies ended in abortion in 2010-14. Globally, 73% (90% UI 59 to 82) of abortions were obtained by married women in 2010-14 compared with 27% (18 to 41) obtained by unmarried women. We did not observe an association between the abortion rates for 2010-14 and the grounds under which abortion is legally allowed.
Interpretation: Abortion rates have declined significantly since 1990 in the developed world but not in the developing world. Ensuring access to sexual and reproductive health care could help millions of women avoid unintended pregnancies and ensure access to safe abortion.
Funding: UK Government, Dutch Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Norwegian Agency for Development Cooperation, The David and Lucile Packard Foundation, UNDP/UNFPA/UNICEF/WHO/World Bank Special Programme of Research, Development and Research Training in Human Reproduction.
Copyright © 2016 World Health Organization. Published by Elsevier Ltd/Inc/BV. All rights reserved. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare no competing interests.
Figures

Comment in
-
Unmet need for abortion and woman-centered contraceptive care.Lancet. 2016 Jul 16;388(10041):216-7. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30452-4. Epub 2016 May 11. Lancet. 2016. PMID: 27179753 No abstract available.
-
Socio-economics: Reduce inequality to reduce abortion.Nature. 2017 Apr 5;544(7648):35. doi: 10.1038/544035d. Nature. 2017. PMID: 28382995 No abstract available.
References
-
- Sedgh G, Singh S, Shah IH, Ahman E, Henshaw SK, Bankole A. Induced abortion: incidence and trends worldwide from 1995 to 2008. Lancet. 2012;379:625–32. - PubMed
-
- Sedgh G, Henshaw S, Singh S, Ahman E, Shah IH. Induced abortion: estimated rates and trends worldwide. Lancet. 2007;370:1338–45. - PubMed
-
- Henshaw SK, Singh S, Haas T. The incidence of abortion worldwide. Int Fam Plan Perspect. 1999;25:44–48. - PubMed
-
- Alkema L, Kantorova V, Menozzi C, Biddlecom A. National, regional, and global rates and trends in contraceptive prevalence and unmet need for family planning between 1990 and 2015: a systematic and comprehensive analysis. Lancet. 2013;381:1642–52. - PubMed
-
- United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. Model-based Estimates and Projections of Family Planning Indicators 2015. New York: United Nations; 2015.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

