Estimating the probability of bacterial infection using a novel biomarker among pediatric patients in the emergency department
- PMID: 27180634
- PMCID: PMC4970211
- DOI: 10.3109/1354750X.2015.1118538
Estimating the probability of bacterial infection using a novel biomarker among pediatric patients in the emergency department
Abstract
Context: IL-27 is a novel biomarker to identify bacterial infection in children.
Objective: IL-27 was evaluated among pediatric emergency department (ED) patients and compared with procalcitonin (PCT).
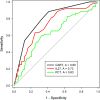
Methods and results: Children undergoing blood, urine, or cerebrospinal fluid cultures had IL-27 and PCT assays performed. Bacterial infection was defined as a positive culture or a clinical diagnosis based on chart review. IL-27 and PCT were increased among patients with bacterial infection and demonstrated comparable AUC's (0.62 versus 0.61). A decision tree incorporating IL-27, PCT, and white blood cell count improved the AUC (0.80).
Conclusion: IL-27 is a viable candidate biomarker to identify bacterial infection among ED patients and is comparable with PCT.
Keywords: IL-27; Interleukin-27; procalcitonin; sepsis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interleukin-27: a novel biomarker in predicting bacterial infection among the critically ill.Crit Care. 2015 Oct 30;19:378. doi: 10.1186/s13054-015-1095-2. Crit Care. 2015. PMID: 26514771 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Use of Procalcitonin Assays to Predict Serious Bacterial Infection in Young Febrile Infants.JAMA Pediatr. 2016 Jan;170(1):62-9. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2015.3210. JAMA Pediatr. 2016. PMID: 26595253
-
C-reactive protein, procalcitonin and the lab-score for detecting serious bacterial infections in febrile children at the emergency department: a prospective observational study.Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2014 Nov;33(11):e273-9. doi: 10.1097/INF.0000000000000466. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2014. PMID: 25093971
-
[Procalcitonin as biomarker for infections].Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2016;160:D282. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2016. PMID: 27734774 Review. Dutch.
-
Procalcitonin as a marker of severe bacterial infection in children in the emergency department.Pediatr Emerg Care. 2010 Jan;26(1):51-60; quiz 61-3. doi: 10.1097/PEC.0b013e3181c399df. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2010. PMID: 20065834 Review.
Cited by
-
Multilevel omics for the discovery of biomarkers in pediatric sepsis.Pediatr Investig. 2023 Nov 21;7(4):277-289. doi: 10.1002/ped4.12405. eCollection 2023 Dec. Pediatr Investig. 2023. PMID: 38050541 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interleukin-27 as a Diagnostic Biomarker for Patients with Sepsis: A Meta-Analysis.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Apr 13;2021:5516940. doi: 10.1155/2021/5516940. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 33954170 Free PMC article.
-
Sepsis Biomarkers.J Pediatr Intensive Care. 2019 Mar;8(1):11-16. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1677537. Epub 2019 Jan 11. J Pediatr Intensive Care. 2019. PMID: 31073503 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cruz AT, Perry AM, Williams EA, Graf JM, Wuestner ER, Patel B. Implementation of goal-directed therapy for children with suspected sepsis in the emergency department. Pediatrics. 2011;127:e758–66. - PubMed
-
- Gomez B, Bressan S, Mintegi S, Da Dalt L, Blazquez D, Olacirequiti I, De La Torre M, Palacios M, Berlese P, Ruano A. Diagnostic value of procalcitonin in well-appearing young febrile infants. Pediatrics. 2012;130:815–22. - PubMed
-
- Haeusler GM, Carlesse F, Phillips RS. An updated systematic review and meta-analysis of the predictive value of serum biomarkers in the assessment of fever during neutropenia in children with cancer. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2013;32:e390–6. - PubMed
-
- Hernandez-Bou S, Trenchs V, Alarcon M, Luaces C. Afebrile very young infants with urinary tract infection and the risk for bacteremia. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2014;33:244–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
