Concurrent Formation of Carbon-Carbon Bonds and Functionalized Graphene by Oxidative Carbon-Hydrogen Coupling Reaction
- PMID: 27181191
- PMCID: PMC4867571
- DOI: 10.1038/srep25824
Concurrent Formation of Carbon-Carbon Bonds and Functionalized Graphene by Oxidative Carbon-Hydrogen Coupling Reaction
Abstract
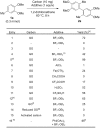
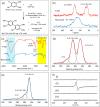
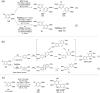
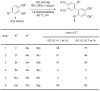
Oxidative C-H coupling reactions were conducted using graphene oxide (GO) as an oxidant. GO showed high selectivity compared with commonly used oxidants such as (diacetoxyiodo) benzene and 2,3-dichloro-5,6-dicyano-p-benzoquinone. A mechanistic study revealed that radical species contributed to the reaction. After the oxidative coupling reaction, GO was reduced to form a material that shows electron conductivity and high specific capacitance. Therefore, this system could concurrently achieve two important reactions: C-C bond formation via C-H transformation and production of functionalized graphene.
Figures
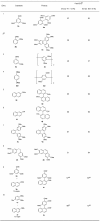
References
-
- Kakiuchi F. & Chatani N. Catalytic methods for C–H bond functionalization: Application in organic synthesis. Adv. Synth. Catal. 345, 1077–1101 (2003).
-
- Godula K. & Sames D. C–H bond functionalization in complex organic synthesis. Science 312, 67–72 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Labinger J. A. & Bercaw J. E. Understanding and exploiting C–H bond activation. Nature 417, 507–514 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Shilov A. E. & Shul’pin G. B. Activation of C–H bonds by metal complexes. Chem. Rev. 97, 2879–2932 (1997). - PubMed
-
- Sarhan A. A. O. & Bolm C. Iron(III) chloride in oxidative C–C coupling reactions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 38, 2730–2744 (2009). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

