RAC1 GTPase promotes the survival of breast cancer cells in response to hyper-fractionated radiation treatment
- PMID: 27181206
- PMCID: PMC5112160
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2016.163
RAC1 GTPase promotes the survival of breast cancer cells in response to hyper-fractionated radiation treatment
Abstract
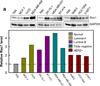
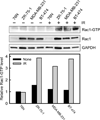
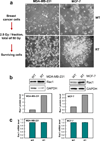
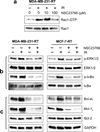
Radiation therapy is a staple approach for cancer treatment, whereas radioresistance of cancer cells remains a substantial clinical problem. In response to ionizing radiation (IR) induced DNA damage, cancer cells can sustain/activate pro-survival signaling pathways, leading to apoptotic resistance and induction of cell cycle checkpoint/DNA repair. Previous studies show that Rac1 GTPase is overexpressed/hyperactivated in breast cancer cells and is associated with poor prognosis. Studies from our laboratory reveal that Rac1 activity is necessary for G2/M checkpoint activation and cell survival in response to IR exposure of breast and pancreatic cancer cells. In this study, we investigated the effect of Rac1 on the survival of breast cancer cells treated with hyper-fractionated radiation (HFR), which is used clinically for cancer treatment. Results in this report indicate that Rac1 protein expression is increased in the breast cancer cells that survived HFR compared with parental cells. Furthermore, this increase of Rac1 is associated with enhanced activities of extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 (ERK1/2) and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signaling pathways and increased levels of anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-xL and Mcl-1, which are downstream targets of ERK1/2 and NF-κB signaling pathways. Using Rac1-specific inhibitor and dominant-negative mutant N17Rac1, here we demonstrate that Rac1 inhibition decreases the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and inhibitory κBα (IκBα), as well as the levels of Bcl-xL and Mcl-1 protein in the HFR-selected breast cancer cells. Moreover, inhibition of Rac1 using either small molecule inhibitor or dominant-negative N17Rac1 abrogates clonogenic survival of HFR-selected breast cancer cells and decreases the level of intact poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase, which is indicative of apoptosis induction. Collectively, results in this report suggest that Rac1 signaling is essential for the survival of breast cancer cells subjected to HFR and implicate Rac1 in radioresistance of breast cancer cells. These studies also provide the basis to explore Rac1 as a therapeutic target for radioresistant breast cancer cells.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTERST The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



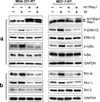
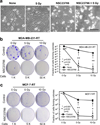

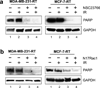
Comment in
-
Rac1 is a potential target to circumvent radioresistance.J Thorac Dis. 2016 Nov;8(11):E1475-E1477. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2016.11.79. J Thorac Dis. 2016. PMID: 28066635 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
RAC1 GTPase plays an important role in γ-irradiation induced G2/M checkpoint activation.Breast Cancer Res. 2012 Apr 11;14(2):R60. doi: 10.1186/bcr3164. Breast Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22494620 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of RAC1 GTPase sensitizes pancreatic cancer cells to γ-irradiation.Oncotarget. 2014 Nov 15;5(21):10251-70. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2500. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 25344910 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear factor-kappaB p65 inhibits mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway in radioresistant breast cancer cells.Mol Cancer Res. 2006 Dec;4(12):945-55. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-06-0291. Mol Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 17189385
-
The Accomplices of NF-κB Lead to Radioresistance.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2015;16(4):279-94. doi: 10.2174/138920371604150429152328. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2015. PMID: 25929862 Review.
-
Relevance of small GTPase Rac1 pathway in drug and radio-resistance mechanisms: Opportunities in cancer therapeutics.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2018 Apr;124:29-36. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2018.01.012. Epub 2018 Feb 4. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2018. PMID: 29548483 Review.
Cited by
-
Rho GTPases in cancer radiotherapy and metastasis.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020 Dec;39(4):1245-1262. doi: 10.1007/s10555-020-09923-5. Epub 2020 Aug 8. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020. PMID: 32772212 Review.
-
PTPσ inhibitors promote hematopoietic stem cell regeneration.Nat Commun. 2019 Aug 14;10(1):3667. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11490-5. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31413255 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptotic and Nonapoptotic Activities of Pterostilbene against Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jan 18;19(1):287. doi: 10.3390/ijms19010287. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29346311 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PR55α-controlled protein phosphatase 2A inhibits p16 expression and blocks cellular senescence induction by γ-irradiation.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Mar 4;16(5):4116-4137. doi: 10.18632/aging.205619. Epub 2024 Mar 4. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 38441530 Free PMC article.
-
The effect and related mechanisms of RAC1 GTP on radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma.Transl Cancer Res. 2025 Jun 30;14(6):3772-3784. doi: 10.21037/tcr-2025-987. Epub 2025 Jun 27. Transl Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40687217 Free PMC article.
References
-
- DeSantis C, Siegel R, Jemal A. Cancer treatment and survivorship: facts and figures 2014–2015. American Cancer Society. 2014–2015:3–6.
-
- Skvortsova I, Debbage P, Kumar V, Skvortsov S. Radiation resistance: Cancer stem cells (CSCs) and their enigmatic pro-survival signaling. Semin Cancer Biol. 2015;35:39–44. - PubMed
-
- Valerie K, Yacoub A, Hagan MP, Curiel DT, Fisher PB, Grant S, et al. Radiation-induced cell signaling: inside-out and outside-in. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007;6:789–801. - PubMed
-
- Sancar A, Lindsey-Boltz LA, Unsal-Kacmaz K, Linn S. Molecular mechanisms of mammalian DNA repair and the DNA damage checkpoints. Annu Rev Biochem. 2004;73:39–85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

