Peroxisomes are platforms for cytomegalovirus' evasion from the cellular immune response
- PMID: 27181750
- PMCID: PMC4867596
- DOI: 10.1038/srep26028
Peroxisomes are platforms for cytomegalovirus' evasion from the cellular immune response
Abstract
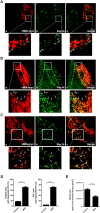
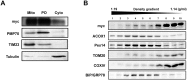
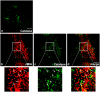
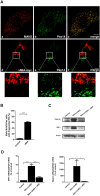
The human cytomegalovirus developed distinct evasion mechanisms from the cellular antiviral response involving vMIA, a virally-encoded protein that is not only able to prevent cellular apoptosis but also to inhibit signalling downstream from mitochondrial MAVS. vMIA has been shown to localize at mitochondria and to trigger their fragmentation, a phenomenon proven to be essential for the signalling inhibition. Here, we demonstrate that vMIA is also localized at peroxisomes, induces their fragmentation and inhibits the peroxisomal-dependent antiviral signalling pathway. Importantly, we demonstrate that peroxisomal fragmentation is not essential for vMIA to specifically inhibit signalling downstream the peroxisomal MAVS. We also show that vMIA interacts with the cytoplasmic chaperone Pex19, suggesting that the virus has developed a strategy to highjack the peroxisomal membrane proteins' transport machinery. Furthermore, we show that vMIA is able to specifically interact with the peroxisomal MAVS. Our results demonstrate that peroxisomes constitute a platform for evasion of the cellular antiviral response and that the human cytomegalovirus has developed a mechanism by which it is able to specifically evade the peroxisomal MAVS-dependent antiviral signalling.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Human Cytomegalovirus vMIA Inhibits MAVS Oligomerization at Peroxisomes in an MFF-Dependent Manner.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Apr 4;10:871977. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.871977. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35445031 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis C virus NS3-4A inhibits the peroxisomal MAVS-dependent antiviral signalling response.J Cell Mol Med. 2016 Apr;20(4):750-7. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12801. Epub 2016 Feb 10. J Cell Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 26865163 Free PMC article.
-
Herpes simplex virus 1 infection dampens the immediate early antiviral innate immunity signaling from peroxisomes by tegument protein VP16.Virol J. 2017 Feb 21;14(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s12985-017-0709-5. Virol J. 2017. PMID: 28222744 Free PMC article.
-
vMIA, a viral inhibitor of apoptosis targeting mitochondria.Biochimie. 2002 Feb-Mar;84(2-3):177-85. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(02)01367-6. Biochimie. 2002. PMID: 12022948 Review.
-
Superresolution imaging of viral protein trafficking.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2015 Jun;204(3):449-60. doi: 10.1007/s00430-015-0395-0. Epub 2015 Feb 28. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25724304 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Interplay between Antiviral Signalling and Carcinogenesis in Human Papillomavirus Infections.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Mar 10;12(3):646. doi: 10.3390/cancers12030646. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32164347 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pex35 is a regulator of peroxisome abundance.J Cell Sci. 2017 Feb 15;130(4):791-804. doi: 10.1242/jcs.187914. Epub 2017 Jan 3. J Cell Sci. 2017. PMID: 28049721 Free PMC article.
-
Dengue and Zika Virus Capsid Proteins Contain a Common PEX19-Binding Motif.Viruses. 2022 Jan 27;14(2):253. doi: 10.3390/v14020253. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35215846 Free PMC article.
-
Peroxisomes and Innate Immunity: Antiviral Response and Beyond.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Aug 3;20(15):3795. doi: 10.3390/ijms20153795. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31382586 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Restructured membrane contacts rewire organelles for human cytomegalovirus infection.Nat Commun. 2022 Aug 11;13(1):4720. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32488-6. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35953480 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mocarski E. S., Shenk T. & Pass R. F. In Fields Virol. (Knipe D. M. & Howley P. M.) 2701–2772 (Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2007).
-
- Goldmacher V. S. Cell death suppression by cytomegaloviruses. Apoptosis 10, 251–65 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

