NMR relaxation and structural elucidation of peptides in the presence and absence of trifluoroethanol illuminates the critical molecular nature of integrin αvβ6 ligand specificity
- PMID: 27182435
- PMCID: PMC4864471
- DOI: 10.1039/C2RA21655H
NMR relaxation and structural elucidation of peptides in the presence and absence of trifluoroethanol illuminates the critical molecular nature of integrin αvβ6 ligand specificity
Abstract
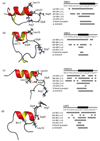
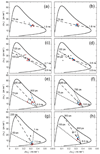
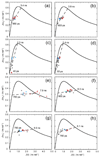
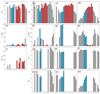
Integrin αvβ6 is an important emerging target for both imaging and therapy of cancer that requires specific ligands based on Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) peptides. There remains little correlation between integrin-RGD ligand specificity despite studies suggesting an RGD-turn-helix ligand motif is required. Here, we describe the application of 15N NMR relaxation analyses and structure determination of αvβ6 peptide ligands in the presence and absence of trifluoroethanol (TFE) to identify their critical molecular nature that influences specificity, interaction and function. Two linear peptides; one known to demonstrate αvβ6 specificity (FMDV2) and the other based on a natural RGD ligand (LAP2), were compared to two additional peptides based on FMDV2 but cyclised in different positions using a disulphide bond (DBD1 and DBD2). The cyclic adaptation in DBD1 produces a significant alteration in backbone dynamic properties when compared to FMDV2; a potential driver for the loss in αvβ6 specificity by DBD1. The importance of ligand dynamics are highlighted through a comprehensive reduced spectral density and ModelFree analysis of peptide 15N NMR relaxation data and suggest αvβ6 specificity requires the formation of a structurally rigid helix preceded by a RGD motif exhibiting slow internal motion. Additional observations include the effect of TFE/water viscosity on global NMR dynamics and the advantages of using spectral density NMR relaxation data to estimate correlation times and motional time regimes for peptides in solution.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Q2DSTD NMR deciphers epitope-mapping variability for peptide recognition of integrin αvβ6.Org Biomol Chem. 2015 Aug 7;13(29):8001-7. doi: 10.1039/c5ob01237f. Epub 2015 Jun 29. Org Biomol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26119198 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the RGD Motif-Containing αvβ6 Integrin-Binding Peptides SFLAP3 and SFITGv6 for Diagnostic Application in HNSCC.J Nucl Med. 2018 Nov;59(11):1679-1685. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.118.210013. Epub 2018 Apr 19. J Nucl Med. 2018. PMID: 29674419
-
Pharmacological Characterization of the αvβ6 Integrin Binding and Internalization Kinetics of the Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus Derived Peptide A20FMDV2.Pharmacology. 2016;97(3-4):114-25. doi: 10.1159/000443180. Epub 2016 Jan 7. Pharmacology. 2016. PMID: 26734728
-
64Cu-1,4,7,10-Tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid-Arg-rich Cys knot scaffold grafted with integrin αvβ6-binding peptide RSLARTDLDHLRGR.2012 Aug 16 [updated 2012 Nov 22]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2012 Aug 16 [updated 2012 Nov 22]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 23193618 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
64Cu-1,4,7,10-Tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid-Arg-rich Cys knot scaffold grafted with integrin αvβ6-binding peptide RSLARTDLDHLRGR.2012 Aug 16 [updated 2012 Nov 29]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2012 Aug 16 [updated 2012 Nov 29]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 23193614 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Tumour targeted contrast enhanced ultrasound imaging dual-modal microbubbles for diagnosis and treatment of triple negative breast cancer.RSC Adv. 2019 Feb 15;9(10):5682-5691. doi: 10.1039/c8ra09737b. eCollection 2019 Feb 11. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35515929 Free PMC article.
-
Q2DSTD NMR deciphers epitope-mapping variability for peptide recognition of integrin αvβ6.Org Biomol Chem. 2015 Aug 7;13(29):8001-7. doi: 10.1039/c5ob01237f. Epub 2015 Jun 29. Org Biomol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26119198 Free PMC article.
-
Optimized serum stability and specificity of an αvβ6 integrin-binding peptide for tumor targeting.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100657. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100657. Epub 2021 Apr 16. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33857478 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hynes RO. Cell. 2002;110:673–687. - PubMed
-
- Morton CA, Campbell I, MacKie RM. The British journal of dermatology. 1996;135:853–855. - PubMed
-
- Kohda D, Morton CJ, Parkar AA, Hatanaka H, Inagaki FM, Campbell ID, Day AJ. Cell. 1996;86:767–775. - PubMed
-
- Morton CJ, Pugh DJ, Brown EL, Kahmann JD, Renzoni DA, Campbell ID. Structure. 1996;4:705–714. - PubMed
-
- Thomas GJ, Lewis MP, Hart IR, Marshall JF, Speight PM. Int J Cancer. 2001;92:641–650. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
