Dual Function of Ccr5 during Langat Virus Encephalitis: Reduction in Neutrophil-Mediated Central Nervous System Inflammation and Increase in T Cell-Mediated Viral Clearance
- PMID: 27183602
- PMCID: PMC4973474
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1502452
Dual Function of Ccr5 during Langat Virus Encephalitis: Reduction in Neutrophil-Mediated Central Nervous System Inflammation and Increase in T Cell-Mediated Viral Clearance
Abstract
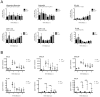
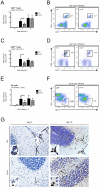
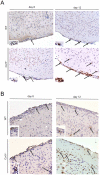
Tick-borne encephalitis virus (TBEV) is a vector-transmitted flavivirus that causes potentially fatal neurologic infection. There are thousands of cases reported annually, and despite the availability of an effective vaccine, the incidence of TBEV is increasing worldwide. Importantly, up to 30% of affected individuals develop long-term neurologic sequelae. We investigated the role of chemokine receptor Ccr5 in a mouse model of TBEV infection using the naturally attenuated tick-borne flavivirus Langat virus (LGTV). Ccr5-deficient mice presented with an increase in viral replication within the CNS and decreased survival during LGTV encephalitis compared with wild-type controls. This enhanced susceptibility was due to the temporal lag in lymphocyte migration into the CNS. Adoptive transfer of wild-type T cells, but not Ccr5-deficient T cells, significantly improved survival outcome in LGTV-infected Ccr5-deficient mice. Concomitantly, a significant increase in neutrophil migration into the CNS in LGTV-infected Ccr5(-/-) mice was documented at the late stage of infection. Ab-mediated depletion of neutrophils in Ccr5(-/-) mice resulted in a significant improvement in mortality, a decrease in viral load, and a decrease in overall tissue damage in the CNS compared with isotype control-treated mice. Ccr5 is crucial in directing T cells toward the LGTV-infected brain, as well as in suppressing neutrophil-mediated inflammation within the CNS.
Copyright © 2016 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Figures
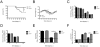
References
-
- Donoso-Mantke O, K.L.S., Ruzek D. InTechOpen. 1st ed. 2011. Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus: A General Overview.
-
- Gritsun TS, Lashkevich VA, Gould EA. Tick-borne encephalitis. Antiviral research. 2003;57:129–146. - PubMed
-
- Suss J. Tick-borne encephalitis in Europe and beyond--the epidemiological situation as of 2007. Euro surveillance : bulletin Europeen sur les maladies transmissibles = European communicable disease bulletin. 2008;13 - PubMed
-
- Ruzek D, Dobler G, Donoso Mantke O. Tick-borne encephalitis: pathogenesis and clinical implications. Travel medicine and infectious disease. 2010;8:223–232. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

