Nuclear delivery of recombinant OCT4 by chitosan nanoparticles for transgene-free generation of protein-induced pluripotent stem cells
- PMID: 27183911
- PMCID: PMC5122344
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.9276
Nuclear delivery of recombinant OCT4 by chitosan nanoparticles for transgene-free generation of protein-induced pluripotent stem cells
Abstract
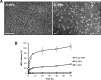
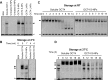
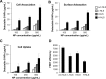
Protein-based reprogramming of somatic cells is a non-genetic approach for the generation of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), whereby reprogramming factors, such as OCT4, SOX2, KLF4 and c-MYC, are delivered as functional proteins. The technique is considered safer than transgenic methods, but, unfortunately, most protein-based protocols provide very low reprogramming efficiencies. In this study, we developed exemplarily a nanoparticle (NP)-based delivery system for the reprogramming factor OCT4. To this end, we expressed human OCT4 in Sf9 insect cells using a baculoviral expression system. Recombinant OCT4 showed nuclear localization in Sf9 cells indicating proper protein folding. In comparison to soluble OCT4 protein, encapsulation of OCT4 in nuclear-targeted chitosan NPs strongly stabilized its DNA-binding activity even under cell culture conditions. OCT4-loaded NPs enabled cell treatment with high micromolar concentrations of OCT4 and successfully delivered active OCT4 into human fibroblasts. Chitosan NPs therefore provide a promising tool for the generation of transgene-free iPSCs.
Keywords: OCT4; chitosan nanoparticles; induced pluripotent stem cells; reprogramming; transgene-free stem cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Using Oct4:MerCreMer Lineage Tracing to Monitor Endogenous Oct4 Expression During the Reprogramming of Fibroblasts into Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs).Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1357:97-110. doi: 10.1007/7651_2015_198. Methods Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 25687297
-
The nuclear receptor Nr5a2 can replace Oct4 in the reprogramming of murine somatic cells to pluripotent cells.Cell Stem Cell. 2010 Feb 5;6(2):167-74. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2009.12.009. Epub 2010 Jan 21. Cell Stem Cell. 2010. PMID: 20096661
-
Reactivation of Endogenous Genes and Epigenetic Remodeling Are Barriers for Generating Transgene-Free Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells in Pig.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 23;11(6):e0158046. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0158046. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27336671 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of Induction: Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs).J Stem Cells. 2015;10(1):43-62. J Stem Cells. 2015. PMID: 26665937 Review.
-
An Insight into DNA-free Reprogramming Approaches to Generate Integration-free Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells for Prospective Biomedical Applications.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2019 Apr;15(2):286-313. doi: 10.1007/s12015-018-9861-6. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2019. PMID: 30417242 Review.
Cited by
-
Cell-Permeable Oct4 Gene Delivery Enhances Stem Cell-like Properties of Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 28;22(17):9357. doi: 10.3390/ijms22179357. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34502264 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Activated Hepatic Stellate Cells Using Collagen-Binding Chitosan Nanoparticles for siRNA Delivery to Fibrotic Livers.Pharmaceutics. 2020 Jun 25;12(6):590. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12060590. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 32630415 Free PMC article.
-
Adult Neural Stem Cells: Basic Research and Production Strategies for Neurorestorative Therapy.Stem Cells Int. 2018 Apr 1;2018:4835491. doi: 10.1155/2018/4835491. eCollection 2018. Stem Cells Int. 2018. PMID: 29760724 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intracellular Delivery of Proteins into Living Cells by Low-Molecular-Weight Polyethyleneimine.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Jun 21;16:4197-4208. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S315444. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 34188469 Free PMC article.
-
Biodegradable and biocompatible high elastic chitosan scaffold is cell-friendly both in vitro and in vivo.Oncotarget. 2017 May 30;8(22):35583-35591. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14709. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28103580 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Takahashi K, Tanabe K, Ohnuki M, Narita M, Ichisaka T, Tomoda K, Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell. 2007;131:861–872. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

