Obstructive sleep apnea and oral language disorders
- PMID: 27184507
- PMCID: PMC9444719
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bjorl.2016.01.017
Obstructive sleep apnea and oral language disorders
Abstract
Introduction: Children and adolescents with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) may have consequences, such as daytime sleepiness and learning, memory, and attention disorders, that may interfere in oral language.
Objective: To verify, based on the literature, whether OSA in children was correlated to oral language disorders.
Methods: A literature review was carried out in the Lilacs, PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science databases using the descriptors "Child Language" AND "Obstructive Sleep Apnea". Articles that did not discuss the topic and included children with other comorbidities rather than OSA were excluded.
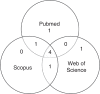
Results: In total, no articles were found at Lilacs, 37 at PubMed, 47 at Scopus, and 38 at Web of Science databases. Based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria, six studies were selected, all published from 2004 to 2014. Four articles demonstrated an association between primary snoring/OSA and receptive language and four articles showed an association with expressive language. It is noteworthy that the articles used different tools and considered different levels of language.
Conclusion: The late diagnosis and treatment of obstructive sleep apnea is associated with a delay in verbal skill acquisition. The professionals who work with children should be alert, as most of the phonetic sounds are acquired during ages 3-7 years, which is also the peak age for hypertrophy of the tonsils and childhood OSA.
Introdução: Crianças e adolescentes com Apneia Obstrutiva do Sono (AOS) podem apresentar sonolência diurna, alterações de aprendizado, memória e atenção, que podem interferir na linguagem oral.
Objetivo: Verificar, com base na literatura, se a AOS apresenta correlação com alterações da linguagem oral.
Método: Foi realizada revisão bibliográfica nas bases de dados Lilacs, Pubmed, Scopus e Web of Science, a partir das palavras-chaves “Linguagem Infantil” AND “Apneia do Sono Tipo Obstrutiva”. Os artigos que não se relacionavam ao tema foram excluídos, bem como estudos com crianças que apresentassem outras comorbidades, além da AOS.
Resultados: Foram localizados 0 artigos na base Lilacs, 37 na Pubmed, 47 na Scopus e 38 na Web of Science. A partir dos critérios de inclusão e exclusão, foram selecionados seis estudos, publicados em 2004 a 2014. Dos artigos incluídos, observou-se em quatro artigos a relação do grupo com ronco primário/SAOS com a Linguagem Receptiva e em quatro artigos a relação dessa população com a Linguagem Expressiva. Ressalta-se que os artigos utilizaram instrumentos diferentes e consideraram níveis diversificados da Linguagem.
Conclusão: O diagnóstico e tratamento tardio de AOS resultam em alterações significantes na qualidade da aquisição verbal. Torna-se imprescindível a atenção dos profissionais que atuam com o a população infantil para este aspecto, uma vez que grande parte dos sons da fala são adquiridos entre 3–7 anos, que corresponde ao período de pico de ocorrência de hipertrofia adenoamigdaliana e AOS na infância.
Keywords: Apneia do sono tipo obstrutiva; Child language; Fonoaudiologia; Language disorders; Linguagem infantil; Obstructive sleep apnea; Speech, language and hearing sciences; Transtornos da linguagem.
Copyright © 2016 Associação Brasileira de Otorrinolaringologia e Cirurgia Cérvico-Facial. Published by Elsevier Editora Ltda. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oral language skills in Brazilian children with obstructive sleep apnea.Res Dev Disabil. 2022 Sep;128:104300. doi: 10.1016/j.ridd.2022.104300. Epub 2022 Jul 8. Res Dev Disabil. 2022. PMID: 35810542
-
Polysomnography in patients with obstructive sleep apnea: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2006;6(13):1-38. Epub 2006 Jun 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2006. PMID: 23074483 Free PMC article.
-
[Expert consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of obstructive sleep apnea in women].Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2024 Jun 12;47(6):509-528. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112147-20240206-00072. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38858201 Chinese.
-
Obstructive sleep apnea, depression and cognitive impairment.Sleep Med. 2020 Aug;72:50-58. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2020.03.017. Epub 2020 Mar 23. Sleep Med. 2020. PMID: 32544796 Review.
-
The role of physical exercise in obstructive sleep apnea.J Bras Pneumol. 2016 Nov-Dec;42(6):457-464. doi: 10.1590/S1806-37562016000000156. J Bras Pneumol. 2016. PMID: 28117479 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Relationship Between Peripheral Arterial Diseases and Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2023 Feb 27;15(2):e35550. doi: 10.7759/cureus.35550. eCollection 2023 Feb. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37007316 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sleep Clinical Record application in Brazilian children and its comparison with Italian children.Sleep Med X. 2019 Aug 8;1:100008. doi: 10.1016/j.sleepx.2019.100008. eCollection 2019 Dec. Sleep Med X. 2019. PMID: 33870167 Free PMC article.
-
Sleep apnea screening through a news portal using the STOP-bang questionnaire.Sleep Breath. 2025 Jan 24;29(1):89. doi: 10.1007/s11325-025-03253-y. Sleep Breath. 2025. PMID: 39853576
-
Unsupervised type III polygraphy in children undergoing adenotonsillectomy: a technical and economic report.Sleep Sci. 2021 Jan-Mar;14(4):370-374. doi: 10.5935/1984-0063.20200094. Sleep Sci. 2021. PMID: 35087635 Free PMC article.
-
A case for the role of memory consolidation in speech-motor learning.Psychon Bull Rev. 2021 Feb;28(1):81-95. doi: 10.3758/s13423-020-01793-w. Psychon Bull Rev. 2021. PMID: 32815112 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- American Academy of Sleep Medicine . 1st ed. Illinois; Westchester: 2007. The AASM manual for the scoring of sleep and associated events: rules, terminology and technical specifications.
-
- Katz E.S., D’Ambrosio C.M. Pediatric obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Clin Chest Med. 2010;31:221–234. - PubMed
-
- Marcus C.L. Pathophysiology of childhood obstructive sleep apnea: current concepts. Resp Physiol. 2000;119:143–154. - PubMed
-
- American Academy of Pediatrics Clinical practice guideline diagnosis and management of childhood obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Pediatrics. 2002;109:704–712. - PubMed
-
- Marcus C.L., Brooks L.J., Draper K.A., Gozal D., Halbower A.C., Jones J., et al. Diagnosis and management of childhood obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Pediatrics. 2012;130:1–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources