Genetic and neuroendocrine regulation of the postpartum brain
- PMID: 27184829
- PMCID: PMC5030130
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2016.05.002
Genetic and neuroendocrine regulation of the postpartum brain
Abstract
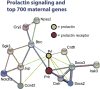
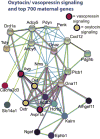
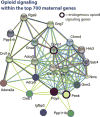
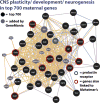
Changes in expression of hundreds of genes occur during the production and function of the maternal brain that support a wide range of processes. In this review, we synthesize findings from four microarray studies of different maternal brain regions and identify a core group of 700 maternal genes that show significant expression changes across multiple regions. With those maternal genes, we provide new insights into reward-related pathways (maternal bonding), postpartum depression, social behaviors, mental health disorders, and nervous system plasticity/developmental events. We also integrate the new genes into well-studied maternal signaling pathways, including those for prolactin, oxytocin/vasopressin, endogenous opioids, and steroid receptors (estradiol, progesterone, cortisol). A newer transcriptional regulation model for the maternal brain is provided that incorporates recent work on maternal microRNAs. We also compare the top 700 genes with other maternal gene expression studies. Together, we highlight new genes and new directions for studies on the postpartum brain.
Keywords: Addiction; Depression; Maternal; Mental health; MicroRNA; Oxytocin; Postpartum; Prolactin; Reward; Social behavior.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures






References
-
- Akbari EM, Shams S, Belay HT, Kaiguo M, Razak Z, Kent CF, Westwood T, Sokolowski MB, Fleming AS. The effects of parity and maternal behavior on gene expression in the medial preoptic area and the medial amygdala in postpartum and virgin female rats: a microarray study. Behav Neurosci. 2013;127:913. - PubMed
-
- Anthony TE, Klein C, Fishell G, Heintz N. Radial glia serve as neuronal progenitors in all regions of the central nervous system. Neuron. 2004;41:881–890. - PubMed
-
- Arbabi L, Baharuldin MTH, Moklas MaM, Fakurazi S, Muhammad SI. Antidepressant-like effects of omega-3 fatty acids in postpartum model of depression in rats. Behav Brain Res. 2014:65–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

