Preventing High Fat Diet-induced Obesity and Improving Insulin Sensitivity through Neuregulin 4 Gene Transfer
- PMID: 27184920
- PMCID: PMC4869101
- DOI: 10.1038/srep26242
Preventing High Fat Diet-induced Obesity and Improving Insulin Sensitivity through Neuregulin 4 Gene Transfer
Abstract
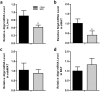
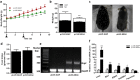
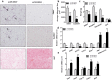
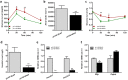
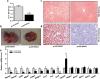
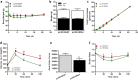
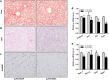
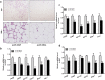
Neuregulin 4 (NRG4), an epidermal growth factor-like signaling molecule, plays an important role in cell-to-cell communication during tissue development. Its function to regulate energy metabolism has recently been reported. This current study was designed to assess the preventive and therapeutic effects of NRG4 overexpression on high fat diet (HFD)-induced obesity. Using the hydrodynamic gene transfer method, we demonstrate that Nrg4 gene transfer in mice suppressed the development of diet-induced obesity, but did not affect pre-existing adiposity and body weight in obese mice. Nrg4 gene transfer curbed HFD-induced hepatic steatosis by inhibiting lipogenesis and PPARγ-mediated lipid storage. Concurrently, overexpression of NRG4 reduced chronic inflammation in both preventive and treatment studies, evidenced by lower mRNA levels of macrophage marker genes including F4/80, Cd68, Cd11b, Cd11c, and macrophage chemokine Mcp1, resulting in improved insulin sensitivity. Collectively, these results demonstrate that overexpression of the Nrg4 gene by hydrodynamic gene delivery prevents HFD-induced weight gain and fatty liver, alleviates obesity-induced chronic inflammation and insulin resistance, and supports the health benefits of NRG4 in managing obesity and obesity-associated metabolic disorders.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The journey towards physiology and pathology: Tracing the path of neuregulin 4.Genes Dis. 2023 Apr 25;11(2):687-700. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2023.03.021. eCollection 2024 Mar. Genes Dis. 2023. PMID: 37692526 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nrg4 promotes fuel oxidation and a healthy adipokine profile to ameliorate diet-induced metabolic disorders.Mol Metab. 2017 Jun 21;6(8):863-872. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2017.03.016. eCollection 2017 Aug. Mol Metab. 2017. PMID: 28752050 Free PMC article.
-
Platycodon grandiflorus Root Extract Attenuates Body Fat Mass, Hepatic Steatosis and Insulin Resistance through the Interplay between the Liver and Adipose Tissue.Nutrients. 2016 Aug 30;8(9):532. doi: 10.3390/nu8090532. Nutrients. 2016. PMID: 27589792 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-6 gene transfer reverses body weight gain and fatty liver in obese mice.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 May;1852(5):1001-11. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2015.01.017. Epub 2015 Feb 4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25660446
-
A systematic review of the association of neuregulin 4, a brown fat-enriched secreted factor, with obesity and related metabolic disturbances.Obes Rev. 2020 Feb;21(2):e12952. doi: 10.1111/obr.12952. Epub 2019 Nov 28. Obes Rev. 2020. PMID: 31782243
Cited by
-
Neuregulin1 ameliorates metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease via the ERK/SIRT1 signaling pathways.BMC Gastroenterol. 2025 Jan 30;25(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s12876-025-03632-5. BMC Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 39885382 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional dynamics in type 2 diabetes progression is linked with circadian, thermogenic, and cellular stress in human adipose tissue.Commun Biol. 2025 Mar 8;8(1):398. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-07709-5. Commun Biol. 2025. PMID: 40057615 Free PMC article.
-
Low circulating levels of neuregulin 4 as a potential biomarker associated with the severity and prognosis of obesity-related metabolic diseases: a systematic review.Adipocyte. 2024 Dec;13(1):2390833. doi: 10.1080/21623945.2024.2390833. Epub 2024 Aug 20. Adipocyte. 2024. PMID: 39162358 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating neuregulin 4 levels are inversely associated with subclinical cardiovascular disease in obese adults.Sci Rep. 2016 Nov 7;6:36710. doi: 10.1038/srep36710. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27819316 Free PMC article.
-
The journey towards physiology and pathology: Tracing the path of neuregulin 4.Genes Dis. 2023 Apr 25;11(2):687-700. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2023.03.021. eCollection 2024 Mar. Genes Dis. 2023. PMID: 37692526 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Harari D. et al.. Neuregulin-4: a novel growth factor that acts through the ErbB-4 receptor tyrosine kinase. Oncogene 18, 2681–2689 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Britsch S. The neuregulin-I/ErbB signaling system in development and disease. Adv. Anat. Embryol. Cell Biol. 190, 1–65 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Hayes N. V. et al.. Expression of neuregulin 4 splice variants in normal human tissues and prostate cancer and their effects on cell motility. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 18, 39–49 (2011). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

