Hedgehog signaling is a potent regulator of liver lipid metabolism and reveals a GLI-code associated with steatosis
- PMID: 27185526
- PMCID: PMC4869931
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.13308
Hedgehog signaling is a potent regulator of liver lipid metabolism and reveals a GLI-code associated with steatosis
Abstract
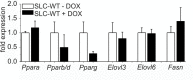
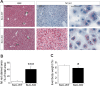
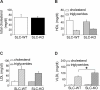
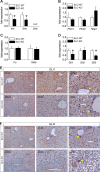
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the most common liver disease in industrialized countries and is increasing in prevalence. The pathomechanisms, however, are poorly understood. This study assessed the unexpected role of the Hedgehog pathway in adult liver lipid metabolism. Using transgenic mice with conditional hepatocyte-specific deletion of Smoothened in adult mice, we showed that hepatocellular inhibition of Hedgehog signaling leads to steatosis by altering the abundance of the transcription factors GLI1 and GLI3. This steatotic 'Gli-code' caused the modulation of a complex network of lipogenic transcription factors and enzymes, including SREBP1 and PNPLA3, as demonstrated by microarray analysis and siRNA experiments and could be confirmed in other steatotic mouse models as well as in steatotic human livers. Conversely, activation of the Hedgehog pathway reversed the "Gli-code" and mitigated hepatic steatosis. Collectively, our results reveal that dysfunctions in the Hedgehog pathway play an important role in hepatic steatosis and beyond.
Keywords: Hedgehog signalling; NAFLD; biochemistry; cell biology; hepatocytes; human; liver; mouse; smoothened; steatotic Gli-code.
Conflict of interest statement
MM-S: GeR is listed as inventor on a patent application filed by the University of Leipzig (WO 2013/110749A1, Therapeutic use of activators of zinc finger protein GLI3).
The other authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures









Similar articles
-
The intrahepatic signalling niche of hedgehog is defined by primary cilia positive cells during chronic liver injury.J Hepatol. 2014 Jan;60(1):143-51. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.08.012. Epub 2013 Aug 23. J Hepatol. 2014. PMID: 23978713
-
Tick-tock hedgehog-mutual crosstalk with liver circadian clock promotes liver steatosis.J Hepatol. 2019 Jun;70(6):1192-1202. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.01.022. Epub 2019 Feb 1. J Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 30711403
-
GLI3-dependent transcriptional repression of Gli1, Gli2 and kidney patterning genes disrupts renal morphogenesis.Development. 2006 Feb;133(3):569-78. doi: 10.1242/dev.02220. Epub 2006 Jan 5. Development. 2006. PMID: 16396903
-
Hepatic Hedgehog signaling contributes to the regulation of IGF1 and IGFBP1 serum levels.Cell Commun Signal. 2014 Feb 18;12:11. doi: 10.1186/1478-811X-12-11. Cell Commun Signal. 2014. PMID: 24548465 Free PMC article.
-
Fuzzy modeling reveals a dynamic self-sustaining network of the GLI transcription factors controlling important metabolic regulators in adult mouse hepatocytes.Mol Biosyst. 2015 Aug;11(8):2190-7. doi: 10.1039/c5mb00129c. Mol Biosyst. 2015. PMID: 26010061
Cited by
-
Cholesterol and Hedgehog Signaling: Mutual Regulation and Beyond.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Apr 27;10:774291. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.774291. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35573688 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of canonical Hedgehog signaling pathway in liver.Int J Biol Sci. 2018 Sep 7;14(12):1636-1644. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.28089. eCollection 2018. Int J Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30416378 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular regulation of mammalian hepatic architecture.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2019;132:91-136. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2018.12.003. Epub 2018 Dec 26. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 30797519 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid metabolism fattens up hedgehog signaling.BMC Biol. 2017 Oct 26;15(1):95. doi: 10.1186/s12915-017-0442-y. BMC Biol. 2017. PMID: 29073896 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact and role of identified long noncoding RNAs in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A narrative review.J Clin Lab Anal. 2023 Jun;37(11-12):e24943. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24943. Epub 2023 Jul 12. J Clin Lab Anal. 2023. PMID: 37435630 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amemiya-Kudo M, Shimano H, Hasty AH, Yahagi N, Yoshikawa T, Matsuzaka T, Okazaki H, Tamura Y, Iizuka Y, Ohashi K, Osuga J, Harada K, Gotoda T, Sato R, Kimura S, Ishibashi S, Yamada N. Transcriptional activities of nuclear srebp-1a, -1c, and -2 to different target promoters of lipogenic and cholesterogenic genes. Journal of Lipid Research. 2002;43:1220–1235. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

