Endothelial HO-1 induction by model TG-rich lipoproteins is regulated through a NOX4-Nrf2 pathway
- PMID: 27185859
- PMCID: PMC4918850
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M067108
Endothelial HO-1 induction by model TG-rich lipoproteins is regulated through a NOX4-Nrf2 pathway
Abstract
Circulating levels of chylomicron remnants (CMRs) increase postprandially and their composition directly reflects dietary lipid intake. These TG-rich lipoproteins likely contribute to the development of endothelial dysfunction, albeit via unknown mechanisms. Here, we investigated how the FA composition of CMRs influences their actions on human aortic endothelial cells (HAECs) by comparing the effects of model CMRs-artificial TG-rich CMR-like particles (A-CRLPs)-containing TGs extracted from fish, DHA-rich algal, corn, or palm oils. HAECs responded with distinct transcriptional programs according to A-CRLP TG content and oxidation status, with genes involved in antioxidant defense and cytoprotection most prominently affected by n-3 PUFA-containing A-CRLPs. These particles were significantly more efficacious inducers of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) than n-6 PUFA corn or saturated FA-rich palm CRLPs. Mechanistically, HO-1 induction by all CRLPs requires NADPH oxidase 4, with PUFA-containing particles additionally dependent upon mitochondrial reactive oxygen species. Activation of both p38 MAPK and PPARβ/δ culminates in increased nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) expression/nuclear translocation and HO-1 induction. These studies define new molecular pathways coupling endothelial cell activation by model CMRs with adaptive regulation of Nrf2-dependent HO-1 expression and may represent key mechanisms through which dietary FAs differentially impact progression of endothelial dysfunction.
Keywords: artificial chylomicron remnant-like particles; cell signaling; endothelial cells; fatty acid; heme oxygenase-1; lipids/oxidation; nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; omega-3 fatty acids; reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase 4; triglyceride.
Copyright © 2016 by the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
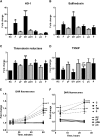
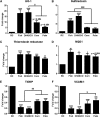
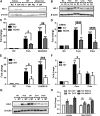


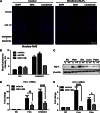

Similar articles
-
Postprandial lipoproteins and the molecular regulation of vascular homeostasis.Prog Lipid Res. 2013 Oct;52(4):446-64. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2013.06.001. Epub 2013 Jun 15. Prog Lipid Res. 2013. PMID: 23774609 Review.
-
Differential influence of different dietary fatty acids on very low-density lipoprotein secretion when delivered to hepatocytes in chylomicron remnants.Metabolism. 2009 Feb;58(2):186-95. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2008.09.012. Metabolism. 2009. PMID: 19154951 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of VLDL secretion by cultured hepatocytes incubated with chylomicron remnants enriched in n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids is regulated by hepatic nuclear factor-4alpha.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 Dec;1791(12):1181-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2009.08.004. Epub 2009 Aug 20. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009. PMID: 19699314
-
Ox-PAPC activation of PMET system increases expression of heme oxygenase-1 in human aortic endothelial cell.J Lipid Res. 2009 Feb;50(2):265-74. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M800317-JLR200. Epub 2008 Aug 29. J Lipid Res. 2009. PMID: 18757839 Free PMC article.
-
Chylomicron remnants: mediators of endothelial dysfunction?Biochem Soc Trans. 2007 Jun;35(Pt 3):442-5. doi: 10.1042/BST0350442. Biochem Soc Trans. 2007. PMID: 17511623 Review.
Cited by
-
New insight into dyslipidemia-induced cellular senescence in atherosclerosis.Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2022 Oct;97(5):1844-1867. doi: 10.1111/brv.12866. Epub 2022 May 15. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2022. PMID: 35569818 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Induction of HO-1 by 5, 8-Dihydroxy-4',7-Dimethoxyflavone via Activation of ROS/p38 MAPK/Nrf2 Attenuates Thrombin-Induced Connective Tissue Growth Factor Expression in Human Cardiac Fibroblasts.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Dec 3;2020:1080168. doi: 10.1155/2020/1080168. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 33343802 Free PMC article.
-
Direct Activation of NADPH Oxidase 2 by 2-Deoxyribose-1-Phosphate Triggers Nuclear Factor Kappa B-Dependent Angiogenesis.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2018 Jan 10;28(2):110-130. doi: 10.1089/ars.2016.6869. Epub 2017 Sep 18. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2018. PMID: 28793782 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Libby P., Ridker P. M., and Hansson G. K.. 2011. Progress and challenges in translating the biology of atherosclerosis. Nature. 473: 317–325. - PubMed
-
- Karpe F., Steiner G., Uffelman K., Olivecrona T., and Hamsten A.. 1994. Postprandial lipoproteins and progression of coronary atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 106: 83–97. - PubMed
-
- Botham K. M., and Wheeler-Jones C. P.. 2013. Postprandial lipoproteins and the molecular regulation of vascular homeostasis. Prog. Lipid Res. 52: 446–464. - PubMed
-
- Bravo E., Napolitano M., and Botham K. M.. 2010. Postprandial lipid metabolism: the missing link between life-style habits and the increasing incidence of metabolic diseases in western countries? Open Transl. Med. J. 2: 1–13.
-
- Nakano T., Nakajima K., Niimi M., Fujita M. Q., Nakajima Y., Takeichi S., Kinoshita M., Matsushima T., Teramoto T., and Tanaka A.. 2008. Detection of apolipoproteins B-48 and B-100 carrying particles in lipoprotein fractions extracted from human aortic atherosclerotic plaques in sudden cardiac death cases. Clin. Chim. Acta. 390: 38–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

