iPARTS2: an improved tool for pairwise alignment of RNA tertiary structures, version 2
- PMID: 27185896
- PMCID: PMC4987943
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkw412
iPARTS2: an improved tool for pairwise alignment of RNA tertiary structures, version 2
Abstract
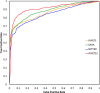
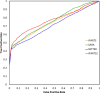
Since its first release in 2010, iPARTS has become a valuable tool for globally or locally aligning two RNA 3D structures. It was implemented by a structural alphabet (SA)-based approach, which uses an SA of 23 letters to reduce RNA 3D structures into 1D sequences of SA letters and applies traditional sequence alignment to these SA-encoded sequences for determining their global or local similarity. In this version, we have re-implemented iPARTS into a new web server iPARTS2 by constructing a totally new SA, which consists of 92 elements with each carrying both information of base and backbone geometry for a representative nucleotide. This SA is significantly different from the one used in iPARTS, because the latter consists of only 23 elements with each carrying only the backbone geometry information of a representative nucleotide. Our experimental results have shown that iPARTS2 outperforms its previous version iPARTS and also achieves better accuracy than other popular tools, such as SARA, SETTER and RASS, in RNA alignment quality and function prediction. iPARTS2 takes as input two RNA 3D structures in the PDB format and outputs their global or local alignments with graphical display. iPARTS2 is now available online at http://genome.cs.nthu.edu.tw/iPARTS2/.
© The Author(s) 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
iPARTS: an improved tool of pairwise alignment of RNA tertiary structures.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Jul;38(Web Server issue):W340-7. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq483. Epub 2010 May 27. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 20507908 Free PMC article.
-
SARSA: a web tool for structural alignment of RNA using a structural alphabet.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Jul 1;36(Web Server issue):W19-24. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn327. Epub 2008 May 23. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18502774 Free PMC article.
-
DIAL: a web server for the pairwise alignment of two RNA three-dimensional structures using nucleotide, dihedral angle and base-pairing similarities.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007 Jul;35(Web Server issue):W659-68. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm334. Epub 2007 Jun 13. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17567620 Free PMC article.
-
Energy-based RNA consensus secondary structure prediction in multiple sequence alignments.Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1097:125-41. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-709-9_7. Methods Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24639158 Review.
-
RNA structures and folding: from conventional to new issues in structure predictions.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1997 Apr;7(2):229-35. doi: 10.1016/s0959-440x(97)80030-9. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1997. PMID: 9094330 Review.
Cited by
-
LocalSTAR3D: a local stack-based RNA 3D structural alignment tool.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Jul 27;48(13):e77. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa453. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32496533 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive survey of long-range tertiary interactions and motifs in non-coding RNA structures.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Sep 8;51(16):8367-8382. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad605. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 37471030 Free PMC article.
-
RMalign: an RNA structural alignment tool based on a novel scoring function RMscore.BMC Genomics. 2019 Apr 8;20(1):276. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-5631-3. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 30961545 Free PMC article.
-
CircularSTAR3D: a stack-based RNA 3D structural alignment tool for circular matching.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 May 22;51(9):e53. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad222. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 36987885 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gesteland R.F., Cech T., Atkins J.F. The RNA world : the Nature of Modern RNA Suggests a Prebiotic RNA World. 3rd edn. NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 2006.
-
- Capriotti E., Marti-Renom M.A. RNA structure alignment by a unit-vector approach. Bioinformatics. 2008;24:112–118. - PubMed
-
- Hoksza D., Svozil D. Efficient RNA pairwise structure comparison by SETTER method. Bioinformatics. 2012;28:1858–1864. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

