Leukotriene E4 elicits respiratory epithelial cell mucin release through the G-protein-coupled receptor, GPR99
- PMID: 27185938
- PMCID: PMC4896673
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1605957113
Leukotriene E4 elicits respiratory epithelial cell mucin release through the G-protein-coupled receptor, GPR99
Abstract
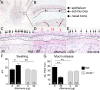
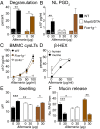
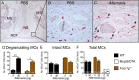
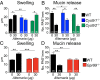
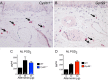
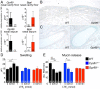
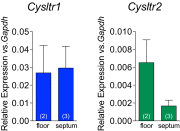
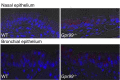
Cysteinyl leukotrienes (cysLTs), leukotriene C4 (LTC4), LTD4, and LTE4 are proinflammatory lipid mediators with pathobiologic function in asthma. LTE4, the stable cysLT, is a weak agonist for the type 1 and type 2 cysLT receptors (CysLTRs), which constrict airway smooth muscle, but elicits airflow obstruction and pulmonary inflammation in patients with asthma. We recently identified GPR99 as a high-affinity receptor for LTE4 that mediates cutaneous vascular permeability. Here we demonstrate that a single intranasal exposure to extract from the respiratory pathogen Alternaria alternata elicits profound epithelial cell (EpC) mucin release and submucosal swelling in the nasal mucosa of mice that depends on cysLTs, as it is absent in mice deficient in the terminal enzyme for cysLT biosynthesis, LTC4 synthase (LTC4S). These mucosal changes are associated with mast cell (MC) activation and absent in MC-deficient mice, suggesting a role for MCs in control of EpC function. Of the three CysLTRs, only GPR99-deficient mice are fully protected from EpC mucin release and swelling elicited by Alternaria or by intranasal LTE4 GPR99 expression is detected on lung and nasal EpCs, which release mucin to doses of LTE4 one log lower than that required to elicit submucosal swelling. Finally, mice deficient in MCs, LTC4S, or GPR99 have reduced baseline numbers of goblet cells, indicating an additional function in regulating EpC homeostasis. These results demonstrate a novel role for GPR99 among CysLTRs in control of respiratory EpC function and suggest that inhibition of LTE4 and of GPR99 may have therapeutic benefits in asthma.
Keywords: cysteinyl leukotrienes; epithelial cell; lung; mast cells; mucosal immunology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wenzel SE, Larsen GL, Johnston K, Voelkel NF, Westcott JY. Elevated levels of leukotriene C4 in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from atopic asthmatics after endobronchial allergen challenge. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990;142(1):112–119. - PubMed
-
- Christie PE, et al. Urinary leukotriene E4 concentrations increase after aspirin challenge in aspirin-sensitive asthmatic subjects. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991;143(5 Pt 1):1025–1029. - PubMed
-
- Drazen JM, et al. Recovery of leukotriene E4 from the urine of patients with airway obstruction. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992;146(1):104–108. - PubMed
-
- Lynch KR, et al. Characterization of the human cysteinyl leukotriene CysLT1 receptor. Nature. 1999;399(6738):789–793. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

