Determining the most effective traits to improve saffron (Crocus sativus L.) yield
- PMID: 27186029
- PMCID: PMC4840151
- DOI: 10.1007/s12298-016-0347-1
Determining the most effective traits to improve saffron (Crocus sativus L.) yield
Abstract
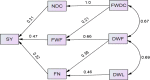
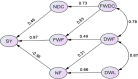
To determine the effective traits to improve saffron yield, a split plot design based on RBCD was done in Mashhad region in Iran for three years (2012-2014). The results showed that all traits except number of daughter corm, fresh weight of daughter corm and dry leaf weight had low general heritability. Results of genotypic and phenotypic coefficients of variation and genetic advance demonstrated that the majority of traits had a low diversity and the selection did not have any effect in improving the traits. As a result, the best way to increase saffron yield is improvement of farm management. It was also found that saffron yield had the highest phenotypic and genotypic correlations with fresh and dry weight of daughter corm and dry and fresh flower weight. Therefore, the efforts to improve these traits will increase saffron yield. According to the present study 5-Jun to 5-Jul was found to be the best sowing date for planting saffron. Also, the Mashhad and Torbat ecotypes were the best ecotypes in this study. Phenotypic and genotypic path analysis showed that in the first step three traits number of daughter corm, fresh flower weight and flower number and in the second step traits fresh weight of daughter corm, dry flower weight and dry leaf weight interred to the regression model and had the highest positive direct and indirect effects on saffron yield. Mainly, it can be derived that the implementation of correct farm management including appropriate sowing date, saffron ecotypes, proper density, bigger and higher quality saffron corm can play an important role in improving yield components and subsequently increasing saffron yield.
Keywords: Cluster analysis; Genetic advance; Heritability; Phenotypic and genotypic path analysis.
Figures
References
-
- Ali MA, Khan IA. Assessment of genetic variation and inheritance mode of some metric traits in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) J Agric Social Sci. 2007;3:112–116.
-
- Ali MA, Nawab NN, Abbas A, Zulkiffal M, Sajjad M. Evaluation of selection criteria in Cicer arietinum L. using correlation coefficients and path analysis. Aust J Crop Sci. 2009;3:65–70.
-
- Amirnia R, Bayat M, Gholamian A. Influence of corm provenance and sowing dates on stigma yield and yield components in saffron (Crocus sativus L.) Turkish Journal Of Field Crops. 2013;18:198–204.
-
- Anastasaki E, Kanakis C, Pappas C, Maggi L, Del Campo C, Carmona M, Alonso G, Polissiou M. Differentiation of saffron from four countries by mid-infrared spectroscopy and multivariate analysis. Eur Food Res Technol. 2010;230:571–577. doi: 10.1007/s00217-009-1197-7. - DOI
-
- Bahraminejad A, Mohammadi-Nejad G, Abdul Khadir M. Genetic Diversity Evaluation of Cumin (‘Cumin cyminum’L.) Based on Phenotypic Characteristics. Aust J Crop Sci. 2011;5(3):304–310.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
