MiR-654-5p attenuates breast cancer progression by targeting EPSTI1
- PMID: 27186421
- PMCID: PMC4859678
MiR-654-5p attenuates breast cancer progression by targeting EPSTI1
Abstract
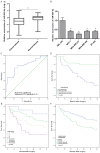
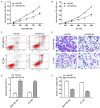
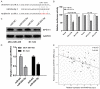
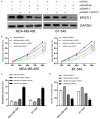
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) dysregulation is a common event in a variety of human diseases including breast cancer. However, clinical relevance and biological role of miR-654-5p in the progression of breast cancer remain greatly elusive. Herein, the expression levels of miR-654-5p were aberrantly downregulated in human breast cancer specimens and four breast cancer cell lines. Low expression of miR-654-5p was strongly associated with advanced TNM stage and lymph node metastasis as well as a poor survival. Functional analysis showed that miR-654-5p overexpression inhibited cell growth and invasion, and induced cell apoptosis in two aggressive breast cancer cells. Further studies demonstrated that Epithelial stromal interaction 1 (EPSTI1) was a direct target gene of miR-654-5p and showed an inverse correlation with miR-654-5p expression. Forced expression of EPSTI1 could abrogate the inhibitory effect of miR-654-5p on the growth and invasion of breast cancer cells as well as apoptosis-induced ability. In conclusion, the present study highlights that miR-654-5p acts as a tumor suppressor in breast cancer through directly targeting EPSTI1, and their functional regulation may open a novel avenue with regard to the therapeutic target for breast cancer.
Keywords: EPSTI1; breast cancer; miR-654-5p; miRNA; survival.
Figures
References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Jones SE. Metastatic breast cancer: the treatment challenge. Clin Breast Cancer. 2008;8:224–233. - PubMed
-
- Steeg PS. Tumor metastasis: mechanistic insights and clinical challenges. Nat Med. 2006;12:895–904. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
