Implementation of a Zebrafish Health Program in a Research Facility: A 4-Year Retrospective Study
- PMID: 27186875
- PMCID: PMC4931741
- DOI: 10.1089/zeb.2015.1230
Implementation of a Zebrafish Health Program in a Research Facility: A 4-Year Retrospective Study
Abstract
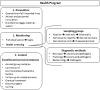
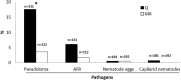
In the past two decades, zebrafish (Danio rerio)-based research has contributed to significant scientific advances. Still, husbandry and health programs did not evolve at the same pace, as evidenced by the absence of general guidelines. Health monitoring is essential to animal welfare, to permit animal exchanges across facilities, to contribute to robust experimental results, and for data reproducibility. In this study, we report a health program implemented in a zebrafish research facility to prevent, monitor, and control pathogen, and disease dissemination. This program includes quarantine, routine health screening of sentinels, and nonroutine screenings of retired animals and sick/moribund individuals. An extensive list of clinical signs, lesions, and pathogens was monitored based on: daily observation of fish, necropsy, histology, and bacterial culture. The results indicate that the combined analysis of sentinels with the evaluation of sick/moribund animals enables a comprehensive description not only of pathogen prevalence but also of clinical and histopathologic lesions of resident animals. The establishment of a quarantine program revealed to be effective in the reduction of Pseudoloma neurophilia frequency in the main aquaria room. Finally, characterization of the colony health status based on this multiapproach program shows a low prevalence of lesions and pathogens in the facility.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Controlling Endemic Pathogens-Challenges and Opportunities.Zebrafish. 2016 Jul;13 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S66-71. doi: 10.1089/zeb.2015.1207. Epub 2016 Mar 16. Zebrafish. 2016. PMID: 26982004 Free PMC article.
-
Facility Design and Health Management Program at the Sinnhuber Aquatic Research Laboratory.Zebrafish. 2016 Jul;13 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S39-43. doi: 10.1089/zeb.2015.1232. Epub 2016 Mar 16. Zebrafish. 2016. PMID: 26981844 Free PMC article.
-
Transmission, diagnosis, and recommendations for control of Pseudoloma neurophilia infections in laboratory zebrafish (Danio rerio) facilities.Comp Med. 2011 Aug;61(4):322-9. Comp Med. 2011. PMID: 22330247 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spores of two fish microsporidia (Pseudoloma neurophilia and Glugea anomala) are highly resistant to chlorine.Dis Aquat Organ. 2007 Jul 16;76(3):205-14. doi: 10.3354/dao076205. Dis Aquat Organ. 2007. PMID: 17803106
-
Review of Pseudoloma neurophilia (Microsporidia): A common neural parasite of laboratory zebrafish (Danio rerio).J Eukaryot Microbiol. 2024 Sep-Oct;71(5):e13040. doi: 10.1111/jeu.13040. Epub 2024 Jul 3. J Eukaryot Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38961716 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Testing Alternative Surface Disinfection Agents for Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Embryos.J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2021 Sep 1;60(5):510-518. doi: 10.30802/AALAS-JAALAS-20-000164. Epub 2021 Aug 20. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2021. PMID: 34416927 Free PMC article.
-
Perceptual mechanisms of social affiliation in zebrafish.Sci Rep. 2020 Feb 27;10(1):3642. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-60154-8. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32107434 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Pronase, Sodium Thiosulfate, and Methylene Blue Combinations on Development and Survival of Sodium Hypochlorite Surface-Disinfected Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Embryos.Zebrafish. 2020 Oct;17(5):342-353. doi: 10.1089/zeb.2020.1917. Zebrafish. 2020. PMID: 33048660 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Water Volume and Bacterial Concentration on the Water Filtration Assay Used in Zebrafish Health Surveillance.J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2021 Nov 1;60(6):655-660. doi: 10.30802/AALAS-JAALAS-21-000004. Epub 2021 Sep 1. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2021. PMID: 34470695 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental Toxicity and Biotransformation of Two Anti-Epileptics in Zebrafish Embryos and Early Larvae.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 24;22(23):12696. doi: 10.3390/ijms222312696. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34884510 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
