Calcific aortic stenosis
- PMID: 27188578
- PMCID: PMC5127286
- DOI: 10.1038/nrdp.2016.6
Calcific aortic stenosis
Abstract
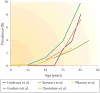
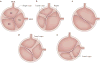
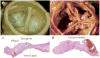
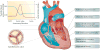
Calcific aortic stenosis (AS) is the most prevalent heart valve disorder in developed countries. It is characterized by progressive fibro-calcific remodelling and thickening of the aortic valve leaflets that, over years, evolve to cause severe obstruction to cardiac outflow. In developed countries, AS is the third-most frequent cardiovascular disease after coronary artery disease and systemic arterial hypertension, with a prevalence of 0.4% in the general population and 1.7% in the population >65 years old. Congenital abnormality (bicuspid valve) and older age are powerful risk factors for calcific AS. Metabolic syndrome and an elevated plasma level of lipoprotein(a) have also been associated with increased risk of calcific AS. The pathobiology of calcific AS is complex and involves genetic factors, lipoprotein deposition and oxidation, chronic inflammation, osteoblastic transition of cardiac valve interstitial cells and active leaflet calcification. Although no pharmacotherapy has proved to be effective in reducing the progression of AS, promising therapeutic targets include lipoprotein(a), the renin-angiotensin system, receptor activator of NF-κB ligand (RANKL; also known as TNFSF11) and ectonucleotidases. Currently, aortic valve replacement (AVR) remains the only effective treatment for severe AS. The diagnosis and staging of AS are based on the assessment of stenosis severity and left ventricular systolic function by Doppler echocardiography, and the presence of symptoms. The introduction of transcatheter AVR in the past decade has been a transformative therapeutic innovation for patients at high or prohibitive risk for surgical valve replacement, and this new technology might extend to lower-risk patients in the near future.
Conflict of interest statement
B.R.L. has received research support from and served on the scientific advisory board for Roche Diagnostics. B.I. has received consultant fees from Abbott and Boehringer Ingelheim and speaker’s fees from Edwards Lifesciences. P.P. has Core Lab contracts with Edwards Lifesciences, for which he receives no direct compensation, and is a speaker for St. Jude Medical. The other authors have no disclosure.
Figures


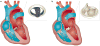
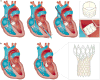
References
-
- Rajamannan NM, Evans FJ, Aikawa E, et al. Calcific aortic valve disease: not simply a degenerative process: a review and agenda for research from the national heart and lung and blood institute aortic stenosis working group * executive summary: calcific aortic valve disease – 2011 update. Circulation. 2011;124:1783–1791. A good review of the state of knowledge (in 2011) and future research directions for calcific aortic valve disease. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Go AS, Mozaffarian D, Roger VL, et al. Executive summary: heart disease and stroke statistics–2013 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2013;127:143–152. - PubMed
-
- Nishimura RA, Otto CM, Bonow RO, et al. 2014 AHA/ACC guideline for the management of patients with valvular heart disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;63:e57–185. Most recent version of the clinical guidelines for the management of valvular heart disease, including aortic stenosis. - PubMed
-
- Vahanian A, Alfieri O, Andreotti F, et al. Guidelines on the management of valvular heart disease (version 2012). Joint task force on the management of valvular heart disease of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC); European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS) Eur Heart J. 2012;33:2451–2496. - PubMed
-
- Roberts WC, Ko JM. Frequency by decades of unicuspid, bicuspid, and tricuspid aortic valves in adults having isolated aortic valve replacement for aortic stenosis, with or without associated aortic regurgitation. Circulation. 2005;111:920–925. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

