Increased concentrations of soluble B7-H3 and interleukin 36 in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of Children with Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia
- PMID: 27188891
- PMCID: PMC4869194
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-016-1555-6
Increased concentrations of soluble B7-H3 and interleukin 36 in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of Children with Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia
Abstract
Background: The purpose of this study is to explore the correlations of interleukin 36 (IL-36) and Soluble B7-H3 (sB7-H3) levels in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) with clinical characteristics and laboratory findings.
Methods: A total of 35 children with M. pneumnoiae pneumonia (MPP) and 15 control subjects were enrolled. BALF concentrations of sB7-H3 and IL-36 were detected using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays and clinical profiles of children with MPP were obtained.
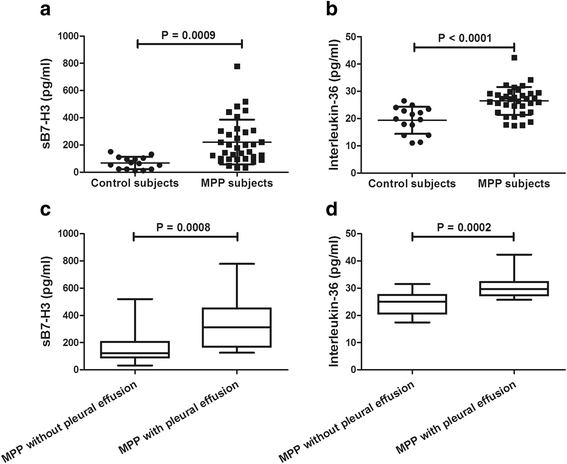
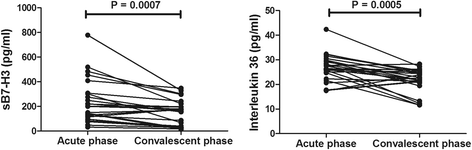
Results: Children with MPP had significantly higher levels of sB7-H3 and IL-36 compared to control subjects (both P < 0.05). Meanwhile, children with pleural effusion had significantly higher levels of sB7-H3 and IL-36 compared to children without pleural effusion (both P < 0.05). BALF concentration of sB7-H3 was strongly associated with concentration of IL-36 (r = 0.796, P < 0.0001) and sB7-H3 was correlated with duration of fever (r = 0.427, P = 0.11) and length of stay (r = 0.345, P = 0.043). Both concentrations of sB7-H3 and IL-36 were significantly decreased in convalescent phase after treatment (both P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Both soluble B7-H3 and IL-36 may play an important role in pathogenesis of M. pneumoniae infection and sB7-H3 could be useful as a prognostic predictor or biomarker of MPP.
Keywords: B7-H3; Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid; Children; Interleukin 36; Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The role of miR-29c/B7-H3/Th17 axis in children with Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia.Ital J Pediatr. 2019 May 14;45(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s13052-019-0655-5. Ital J Pediatr. 2019. PMID: 31088519 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble B7-H3 elevations in hospitalized children with Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2013 Dec;77(4):362-6. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2013.09.006. Epub 2013 Oct 17. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2013. PMID: 24139879
-
Plasma soluble B7-H3 levels for severity evaluation in pediatric patients with Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia.Int Immunopharmacol. 2019 Aug;73:163-171. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.05.014. Epub 2019 May 14. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31100711
-
Atypical pathogen community-acquired pneumonia: an analysis of clinical characteristics, drug treatment, and prognosis in the related patients.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Mar 14;52(1):309. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10382-w. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40085176 Review.
-
Biomarkers associated with the diagnosis and prognosis of Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children: a review.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Mar 18;15:1552144. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1552144. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40171163 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Novel Functional eQTL-SNPs Associated With Susceptibility to Mycoplasma pneumoniae Pneumonia in Children.Front Public Health. 2022 Jun 28;10:899045. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.899045. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35836993 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-36: Structure, Signaling and Function.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;21:191-210. doi: 10.1007/5584_2020_488. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 32026417 Review.
-
Exhausted and Apoptotic BALF T Cells in Proinflammatory Airway Milieu at Acute Phase of Severe Mycoplasma Pneumoniae Pneumonia in Children.Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 17;12:760488. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.760488. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35111152 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoregulatory protein B7-H3 upregulated in bacterial and viral infection and its diagnostic potential in clinical settings.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 21;15:1472626. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1472626. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39497833 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

