Tian Jiu therapy for allergic rhinitis: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 27189087
- PMCID: PMC4869399
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-016-1374-5
Tian Jiu therapy for allergic rhinitis: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Allergic rhinitis (AR) is one of the most common allergic diseases. The conventional treatments of allergic rhinitis are oral anti-histamines, the use of intranasal corticosteroids, and immunotherapy. Dissatisfied with the ineffectiveness and side effects of these treatments, substantial numbers of patients are turning to alternative treatments like Chinese herbal medicine, particularly Tian Jiu (TJ). TJ is a form of moxibustion in which herbal patches are applied to specific acupoints on the skin. This study aims to investigate the efficacy and safety of TJ in the treatment of allergic rhinitis.
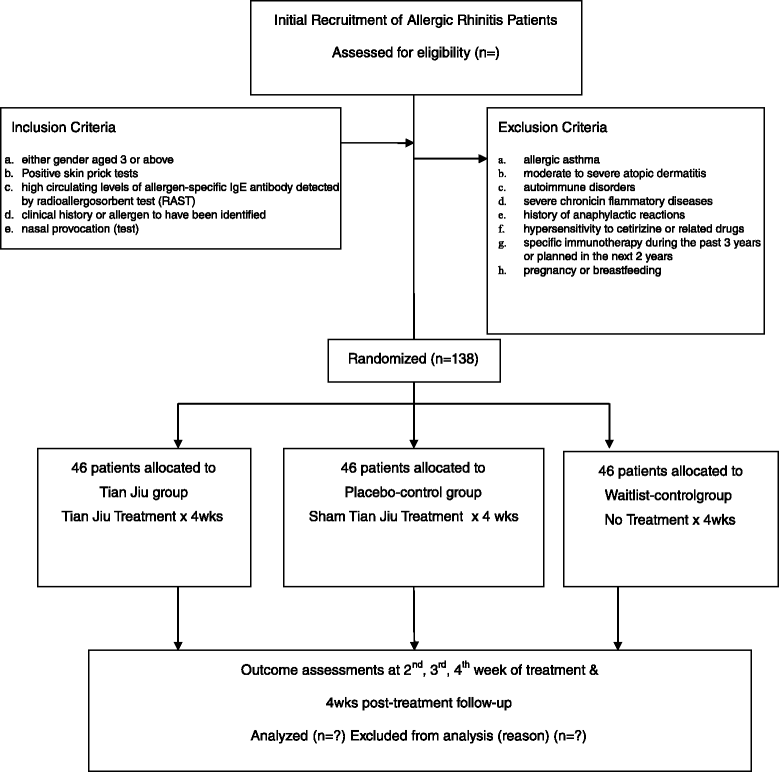
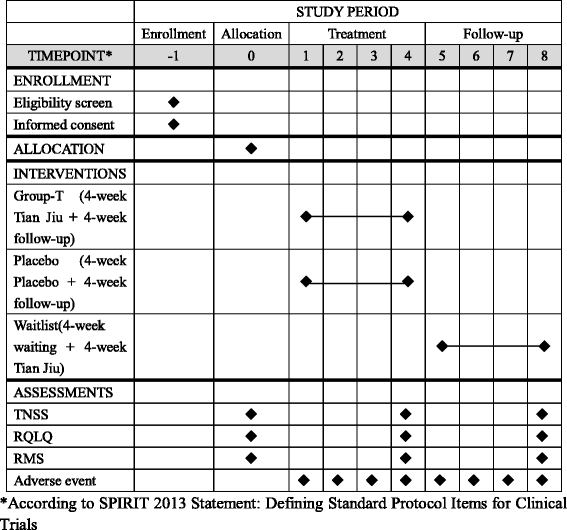
Methods/design: This will be a prospective, randomized, single-blinded, controlled trial in patients with AR. After a 1-week run-in period, eligible subjects will be randomly assigned to the TJ group, placebo-control group or waitlist-control group. The TJ and placebo-control groups will undergo a 4-week treatment with one session per week and one 4-week post-treatment follow-up. Participants in the waitlist-control group will not receive any treatment during the first 4 weeks but will be required to be assessed. The primary outcome will be the change in the weekly average of the Total Nasal Symptom Score recorded from baseline to the end of treatment. The secondary outcomes will be change in symptoms and change in need for medication between baseline and the end of treatment by using the Rhinitis Quality of Life Questionnaire. Rescue medication (RM) needs will be measured using an RM score, comprising the weekly sum of daily assessments and any form of systemic steroids for allergic rhinitis.
Discussion: This study will be the first study to compare TJ treatment for allergic rhinitis with a placebo-control group, and a waitlist-control group. The investigation of TJ for allergic rhinitis will also suggest recommendations for clinical practice. The results of this study are expected to provide consolidated evidence for the effectiveness and safety of TJ for the treatment of patients with allergic rhinitis.
Trial registration: NCT02470845 (17 May 2015).
Keywords: Allergic rhinitis; Chinese herbal medicine; Randomized controlled trial; Tian Jiu.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of using a warming needle for persistent allergic rhinitis: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2016 Jun 30;17(1):305. doi: 10.1186/s13063-016-1432-z. Trials. 2016. PMID: 27363578 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Sphenopalatine ganglion stimulation with one acupuncture needle for moderate-severe persistent allergic rhinitis: study protocol for a multicenter randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2015 Apr 23;16:183. doi: 10.1186/s13063-015-0707-0. Trials. 2015. PMID: 25899566 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Chinese herbal medicine bi min fang for allergic rhinitis: protocol for a double-blind, double-dummy, randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2019 Jan 18;20(1):66. doi: 10.1186/s13063-018-3151-0. Trials. 2019. PMID: 30658660 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of endonasal phototherapy for relieving the symptoms of allergic rhinitis: Meta-analysis.Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2015 Jul-Aug;29(4):283-91. doi: 10.2500/ajra.2015.29.4190. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2015. PMID: 26163248
-
Treatment of allergic rhinitis using mobile technology with real-world data: The MASK observational pilot study.Allergy. 2018 Sep;73(9):1763-1774. doi: 10.1111/all.13406. Epub 2018 Mar 22. Allergy. 2018. PMID: 29336067 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the Relationship between Allergic Rhinitis and Constitution Based on the "Traditional Chinese Medicine Constitution Theory".Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Aug 24;2022:9230317. doi: 10.1155/2022/9230317. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 36062169 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An External CAM Therapy (Tian Jiu) versus Placebo in Treatment of Allergic Rhinitis: A Pilot Single-Blinded, Three-Arm, Randomized Controlled Study.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019 Apr 14;2019:6369754. doi: 10.1155/2019/6369754. eCollection 2019. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019. PMID: 31097971 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials