Zinc isotope ratios of bones and teeth as new dietary indicators: results from a modern food web (Koobi Fora, Kenya)
- PMID: 27189145
- PMCID: PMC4870686
- DOI: 10.1038/srep26281
Zinc isotope ratios of bones and teeth as new dietary indicators: results from a modern food web (Koobi Fora, Kenya)
Abstract
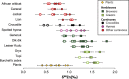
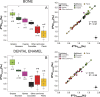
In order to explore the possibilities of using zinc (Zn) stable isotope ratios as dietary indicators, we report here on the measurements of the ratio of stable isotopes of zinc ((66)Zn/(64)Zn, expressed here as δ(66)Zn) in bioapatite (bone and dental enamel) of animals from a modern food web in the Koobi Fora region of the Turkana Basin in Kenya. We demonstrate that δ(66)Zn values in both bone and enamel allow a clear distinction between carnivores and herbivores from this food web. Differences were also observed between browsers and grazers as well as between carnivores that consumed bone (i.e. hyenas) compared to those that largely consume flesh (i.e. lions). We conclude that Zn isotope ratio measurements of bone and teeth are a new and promising dietary indicator.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Copper and zinc isotope ratios in human bone and enamel.Am J Phys Anthropol. 2017 Mar;162(3):491-500. doi: 10.1002/ajpa.23132. Epub 2016 Nov 17. Am J Phys Anthropol. 2017. PMID: 27858983
-
Zinc Isotope Ratios as Indicators of Diet and Trophic Level in Arctic Marine Mammals.PLoS One. 2016 Mar 24;11(3):e0152299. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152299. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27010907 Free PMC article.
-
Zinc isotopes in Late Pleistocene fossil teeth from a Southeast Asian cave setting preserve paleodietary information.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Mar 3;117(9):4675-4681. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1911744117. Epub 2020 Feb 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32071235 Free PMC article.
-
Variation in the isotopic composition of zinc in the natural environment and the use of zinc isotopes in biogeosciences: a review.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2008 Jan;390(2):451-63. doi: 10.1007/s00216-007-1635-y. Epub 2007 Oct 19. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2008. PMID: 17952419 Review.
-
Reconstruction of breastfeeding and weaning practices using stable isotope and trace element analyses: A review.Am J Phys Anthropol. 2015 Feb;156 Suppl 59:2-21. doi: 10.1002/ajpa.22657. Epub 2014 Nov 19. Am J Phys Anthropol. 2015. PMID: 25407359 Review.
Cited by
-
Isotopic Evidence for Disrupted Copper Metabolism in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis.iScience. 2018 Aug 31;6:264-271. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2018.07.023. Epub 2018 Aug 1. iScience. 2018. PMID: 30240616 Free PMC article.
-
Historical overview and new directions in bioarchaeological trace element analysis: a review.Archaeol Anthropol Sci. 2021;13(1):24. doi: 10.1007/s12520-020-01262-4. Epub 2021 Jan 15. Archaeol Anthropol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33520004 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur elemental and isotopic variations in mouse hair and bone collagen during short-term graded calorie restriction.iScience. 2024 May 22;27(6):110059. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110059. eCollection 2024 Jun 21. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38947513 Free PMC article.
-
Reliable and precise Zn isotopic analysis of biological matrices using a fully automated dual-column purification procedure.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2025 Feb;417(4):835-846. doi: 10.1007/s00216-024-05702-1. Epub 2024 Dec 23. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2025. PMID: 39710783
-
The Distribution and Biogenic Origins of Zinc in the Mineralised Tooth Tissues of Modern and Fossil Hominoids: Implications for Life History, Diet and Taphonomy.Biology (Basel). 2023 Nov 21;12(12):1455. doi: 10.3390/biology12121455. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38132281 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chu N.-C., Henderson G. M., Belshaw N. S. & Hedges R. E. Establishing the potential of Ca isotopes as proxy for consumption of dairy products. Appl. Geochem. 21, 1656–1667 (2006).
-
- Knudson K. J. et al.. Introducing δ88/86Sr analysis in archaeology: a demonstration of the utility of strontium isotope fractionation in paleodietary studies. J. Archaeol. Sci. 37, 2352–2364 (2010).
-
- Jaouen K., Pons M.-L. & Balter V. Iron, copper and zinc isotopic fractionation up mammal trophic chains. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 374, 164–172 (2013).
-
- Martin J. E., Vance D. & Balter V. Natural variation of magnesium isotopes in mammal bones and teeth from two South African trophic chains. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 130, 12–20 (2014).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

