Optimisation of DNA extraction from the crustacean Daphnia
- PMID: 27190714
- PMCID: PMC4867708
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.2004
Optimisation of DNA extraction from the crustacean Daphnia
Abstract
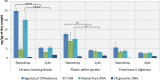
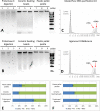
Daphnia are key model organisms for mechanistic studies of phenotypic plasticity, adaptation and microevolution, which have led to an increasing demand for genomics resources. A key step in any genomics analysis, such as high-throughput sequencing, is the availability of sufficient and high quality DNA. Although commercial kits exist to extract genomic DNA from several species, preparation of high quality DNA from Daphnia spp. and other chitinous species can be challenging. Here, we optimise methods for tissue homogenisation, DNA extraction and quantification customised for different downstream analyses (e.g., LC-MS/MS, Hiseq, mate pair sequencing or Nanopore). We demonstrate that if Daphnia magna are homogenised as whole animals (including the carapace), absorbance-based DNA quantification methods significantly over-estimate the amount of DNA, resulting in using insufficient starting material for experiments, such as preparation of sequencing libraries. This is attributed to the high refractive index of chitin in Daphnia's carapace at 260 nm. Therefore, unless the carapace is removed by overnight proteinase digestion, the extracted DNA should be quantified with fluorescence-based methods. However, overnight proteinase digestion will result in partial fragmentation of DNA therefore the prepared DNA is not suitable for downstream methods that require high molecular weight DNA, such as PacBio, mate pair sequencing and Nanopore. In conclusion, we found that the MasterPure DNA purification kit, coupled with grinding of frozen tissue, is the best method for extraction of high molecular weight DNA as long as the extracted DNA is quantified with fluorescence-based methods. This method generated high yield and high molecular weight DNA (3.10 ± 0.63 ng/µg dry mass, fragments >60 kb), free of organic contaminants (phenol, chloroform) and is suitable for large number of downstream analyses.
Keywords: Epigenetics; Genomics; High throughput sequencing; Omics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Azofeifa DE, Arguedas HJ, Vargas WE. Optical properties of chitin and chitosan biopolymers with application to structural color analysis. Optical Materials. 2012;35:175–183. doi: 10.1016/j.optmat.2012.07.024. - DOI
-
- Brakovska A, Škute N. Optimisation of DNA extraction and RAPD-PCR amplification for population genetic analysis of Daphnia cucullata Sars, 1862 (Crustacea: Cladocera) Acta Biologica Universitatis Daugavpiliensis. 2013;13:11–20.
-
- Colbourne JK, Pfrender ME, Gilbert D, Thomas WK, Tucker A, Oakley TH, Tokishita S, Aerts A, Arnold GJ, Basu MK, Bauer DJ, Cáceres CE, Carmel L, Casola C, Choi JH, Detter JC, Dong Q, Dusheyko S, Eads BD, Fröhlich T, Geiler-Samerotte KA, Gerlach D, Hatcher P, Jogdeo S, Krijgsveld J, Kriventseva EV, Kültz D, Laforsch C, Lindquist E, Lopez J, Manak JR, Muller J, Pangilinan J, Patwardhan RP, Pitluck S, Pritham EJ, Rechtsteiner A, Rho M, Rogozin IB, Sakarya O, Salamov A, Schaack S, Shapiro H, Shiga Y, Skalitzky C, Smith Z, Souvorov A, Sung W, Tang Z, Tsuchiya D, Tu H, Vos H, Wang M, Wolf YI, Yamagata H, Yamada T, Ye Y, Shaw JR, Andrews J, Crease TJ, Tang H, Lucas SM, Robertson HM, Bork P, Koonin EV, Zdobnov EM, Grigoriev IV, Lynch M, Boore JL. The ecoresponsive genome of Daphnia pulex. Science. 2011;331:555–561. doi: 10.1126/science.1197761. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dircksen H, Neupert S, Predel R, Verleyen P, Huybrechts J, Strauss J, Hauser F, Stafflinger E, Schneider M, Pauwels K, Schoofs L, Grimmelikhuijzen CJP. Genomics, transcriptomics, and peptidomics of Daphnia pulex neuropeptides and protein hormones. Journal of Proteome Research. 2011;10:4478–4504. doi: 10.1021/pr200284e. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

