Responsiveness to IL-7 but not to IFN-α is diminished in CD4+ T cells from treated HIV infected patients who experience poor CD4+ T-cell recovery
- PMID: 27191978
- PMCID: PMC5022566
- DOI: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000001161
Responsiveness to IL-7 but not to IFN-α is diminished in CD4+ T cells from treated HIV infected patients who experience poor CD4+ T-cell recovery
Abstract
Objective: To assess CD4 T-cell responsiveness to IL-7 and IFN-α in HIV-infected patients who experience poor recovery of CD4 T-cell counts during therapy (immune failure patients).
Design: Responses to IL-7 and IFN-α were compared between HIV-infected immune failure (CD4 cell counts <379 cells/μl) patients and immune success (CD4 cell counts >500 cells/μl) as well as healthy control patients.
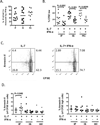
Methods: Flow cytometry was used to assess peripheral blood mononuclear cells for IL-7-induced proliferation, CD25 expression, and signaling (signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 phosphorylation and Akt phosphorylation) in CD4 T cells. Freshly isolated cells were characterized by expression of IL-7Rα (CD127) among CD4 T-cell maturation subsets by flow cytometry and sorted CD3 T cells were assessed for expression of IFN-α and interferon stimulated genes (2'-5'-oligoadenylate synthetase-1 and myxovirus resistance A protein) by quantitative real-time PCR. Responses to IFN-α were assessed by induction of signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 phosphorylation and inhibition of IL-7-induced CD4 T-cell proliferation.
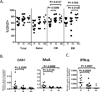
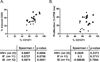
Results: IL-7-induced proliferation and CD25 expression were decreased in CD4 T cells from immune failure patients. CD127 expressing CD4 T cells were decreased, whereas expression of 2'-5'-oligoadenylate synthetase-1, myxovirus resistance A protein, and IFN-α mRNA were increased in total CD3 T cells from immune failure patients. CD127 expression correlated with CD25 induction but not proliferation, whereas T-cell IFN-α mRNA was associated with reduced proliferation in CD4 T cells from immune failure patients. IFN-α-mediated induction of signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 phosphorylation and inhibition of proliferation were not diminished in CD4 T cells from immune failure patients.
Conclusion: IL-7 responsiveness is impaired in immune failure patients and may be related to expression of CD127 and IFN-α.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
IFN-α exerts opposing effects on activation-induced and IL-7-induced proliferation of T cells that may impair homeostatic maintenance of CD4+ T cell numbers in treated HIV infection.J Immunol. 2014 Sep 1;193(5):2178-86. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1302536. Epub 2014 Jul 25. J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25063872 Clinical Trial.
-
Interleukin-7 signalling defects in naive CD4+ T cells of HIV patients with CD4+ T-cell deficiency on antiretroviral therapy are associated with T-cell activation and senescence.AIDS. 2014 Mar 27;28(6):821-30. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000000213. AIDS. 2014. PMID: 24499954
-
Biological determinants of immune reconstitution in HIV-infected patients receiving antiretroviral therapy: the role of interleukin 7 and interleukin 7 receptor α and microbial translocation.J Infect Dis. 2010 Oct 15;202(8):1254-64. doi: 10.1086/656369. J Infect Dis. 2010. PMID: 20812848
-
The influence of HIV on CD127 expression and its potential implications for IL-7 therapy.Semin Immunol. 2012 Jun;24(3):231-40. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2012.02.006. Epub 2012 Mar 14. Semin Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22421574 Review.
-
Advances in Mechanism of HIV-1 Immune Reconstitution Failure: Understanding Lymphocyte Subpopulations and Interventions for Immunological Nonresponders.J Immunol. 2024 Jun 1;212(11):1609-1620. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2300777. J Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38768409 Review.
Cited by
-
SAMHD1 expression is associated with low immune activation but not correlated with HIV‑1 DNA levels in CD4+ T cells of patients with HIV‑1.Mol Med Rep. 2020 Aug;22(2):879-885. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11153. Epub 2020 May 18. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 32468062 Free PMC article.
-
IL7RA genetic variants differentially affect IL-7Rα expression and alternative splicing: a role in autoimmune and infectious diseases?Genes Immun. 2020 Feb;21(2):83-90. doi: 10.1038/s41435-019-0091-y. Epub 2020 Jan 13. Genes Immun. 2020. PMID: 31929513 Review.
-
Increased Regulatory T-Cell Activity and Enhanced T-Cell Homeostatic Signaling in Slow Progressing HIV-infected Children.Front Immunol. 2019 Feb 12;10:213. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00213. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30809229 Free PMC article.
-
Naïve/Effector CD4 T cell ratio as a useful predictive marker of immune reconstitution in late presenter HIV patients: A multicenter study.PLoS One. 2019 Dec 23;14(12):e0225415. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0225415. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31869342 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant plasma IL-7 and soluble IL-7 receptor levels indicate impaired T-cell response to IL-7 in human tuberculosis.PLoS Pathog. 2017 Jun 5;13(6):e1006425. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006425. eCollection 2017 Jun. PLoS Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28582466 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gazzola L, Tincati C, Bellistri GM, Monforte A, Marchetti G. The absence of CD4+ T cell count recovery despite receipt of virologically suppressive highly active antiretroviral therapy: clinical risk, immunological gaps, and therapeutic options. Clin Infect Dis. 2009;48:328–337. - PubMed
-
- Lichtenstein KA, Ward DJ, Moorman AC, Delaney KM, Young B, Palella FJ, Jr, et al. Clinical assessment of HIV-associated lipodystrophy in an ambulatory population. AIDS. 2001;15:1389–1398. - PubMed
-
- Yong MK, Elliott JH, Woolley IJ, Hoy JF. Low CD4 count is associated with an increased risk of fragility fracture in HIV-infected patients. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2011;57:205–210. - PubMed
-
- Grulich AE, van Leeuwen MT, Falster MO, Vajdic CM. Incidence of cancers in people with HIV/AIDS compared with immunosuppressed transplant recipients: a meta-analysis. Lancet. 2007;370:59–67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

