Compaction and segregation of sister chromatids via active loop extrusion
- PMID: 27192037
- PMCID: PMC4914367
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.14864
Compaction and segregation of sister chromatids via active loop extrusion
Abstract
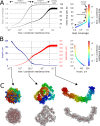
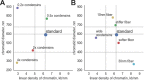
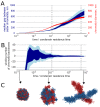
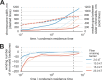
The mechanism by which chromatids and chromosomes are segregated during mitosis and meiosis is a major puzzle of biology and biophysics. Using polymer simulations of chromosome dynamics, we show that a single mechanism of loop extrusion by condensins can robustly compact, segregate and disentangle chromosomes, arriving at individualized chromatids with morphology observed in vivo. Our model resolves the paradox of topological simplification concomitant with chromosome 'condensation', and explains how enzymes a few nanometers in size are able to control chromosome geometry and topology at micron length scales. We suggest that loop extrusion is a universal mechanism of genome folding that mediates functional interactions during interphase and compacts chromosomes during mitosis.
Keywords: biophysics; chromosome; chromosomes; compaction; genes; molecular dynamics; none; polymer; simulations; structural biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Ball RC, Marko JF, Milner ST, Witten TA. Polymers grafted to a convex surface. Macromolecules. 1991;24:693–703. doi: 10.1021/ma00003a011. - DOI
-
- Birshtein TM, Borisov OV, Zhulina YB, Khokhlov AR, Yurasova TA. Conformations of comb-like macromolecules. Polymer Science U.S.S.R. 1987;29:1293–1300. doi: 10.1016/0032-3950(87)90374-1. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

