Susceptibility-weighted imaging: current status and future directions
- PMID: 27192086
- PMCID: PMC5116013
- DOI: 10.1002/nbm.3552
Susceptibility-weighted imaging: current status and future directions
Abstract
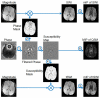
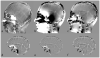
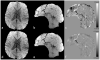
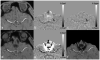
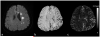
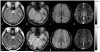
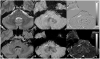
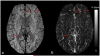
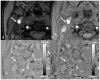
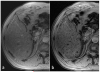
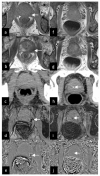
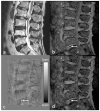
Susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI) is a method that uses the intrinsic nature of local magnetic fields to enhance image contrast in order to improve the visibility of various susceptibility sources and to facilitate diagnostic interpretation. It is also the precursor to the concept of the use of phase for quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM). Nowadays, SWI has become a widely used clinical tool to image deoxyhemoglobin in veins, iron deposition in the brain, hemorrhages, microbleeds and calcification. In this article, we review the basics of SWI, including data acquisition, data reconstruction and post-processing. In particular, the source of cusp artifacts in phase images is investigated in detail and an improved multi-channel phase data combination algorithm is provided. In addition, we show a few clinical applications of SWI for the imaging of stroke, traumatic brain injury, carotid vessel wall, siderotic nodules in cirrhotic liver, prostate cancer, prostatic calcification, spinal cord injury and intervertebral disc degeneration. As the clinical applications of SWI continue to expand both in and outside the brain, the improvement of SWI in conjunction with QSM is an important future direction of this technology. Copyright © 2016 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Keywords: cerebral microbleeds; multi-channel phase data combination; phase imaging; quantitative susceptibility mapping; stroke; susceptibility-weighted imaging.
Copyright © 2016 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Figures
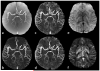

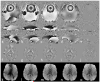
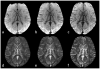
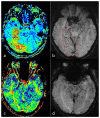
References
-
- Haacke EM, Lai S, Yablonskiy DA, Lin W. In vivo validation of the bold mechanism: A review of signal changes in gradient echo functional MRI in the presence of flow. Int J Imaging Syst Technol. 1995;6(2-3):153–63.
-
- Haacke EM, Lai S, Reichenbach JR, Kuppusamy K, Hoogenraad FG, Takeichi H, Lin W. In vivo measurement of blood oxygen saturation using magnetic resonance imaging: a direct validation of the blood oxygen level-dependent concept in functional brain imaging. Hum Brain Mapp. 1997;5(5):341–6. - PubMed
-
- Reichenbach JR, Venkatesan R, Schillinger DJ, Kido DK, Haacke EM. Small vessels in the human brain: MR venography with deoxyhemoglobin as an intrinsic contrast agent. Radiology. 1997;204(1):272–7. - PubMed
-
- Reichenbach JR, Essig M, Haacke EM, Lee BC, Przetak C, Kaiser WA, Schad LR. High-resolution venography of the brain using magnetic resonance imaging. MAGMA. 1998;6(1):62–9. - PubMed
-
- Reichenbach JR, Barth M, Haacke EM, Klarhöfer M, Kaiser WA, Moser E. High-resolution MR venography at 3.0 Tesla. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2000;24(6):949–57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

