Paronychia and granulation tissue formation during treatment with isotretinoin
- PMID: 27192525
- PMCID: PMC4861573
- DOI: 10.1590/abd1806-4841.20163817
Paronychia and granulation tissue formation during treatment with isotretinoin
Abstract
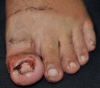
This paper describes the association of two unusual side effects of treatment with isotretinoin for severe acne: paronychia and excess granulation tissue in the nails furrows. We report a case of male patient aged 19 years, who in the course of the 36th week of treatment with isotretinoin for acne grade III showed erythema, edema, excess granulation tissue and onychocryptosis in various nail beds of hands and feet, with no history of trauma associated. A literature review revealed few reports of these adverse events, and two clinical patterns of exuberant granulation tissue has been described: one in periungual location and other in lesions of previous acne. The rarity and lack of knowledge on the best treatment for granuloma-like reactions make this theme a considerable challenge.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: None.
Figures



References
-
- Exner JH, Dahod S, Pochi PE. Pyogenic granuloma-like acne lesions during isotretinoin therapy. Arch Dermatol. 1983;119:808–811. - PubMed
-
- Brelsford M, Beute TC. Preventing and managing the side effects of isotretinoin. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2008;27:197–206. - PubMed
-
- Charakida A, Mouser PE, Chu AC. Safety and side effects of the acne drug, oral isotretinoin. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2004;3:119–129. - PubMed
-
- Bigby M, Stern RS. Adverse reactions to isotretinoin. A report from the Adverse Drug Reaction Reporting System. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1988;18:543–552. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
