CD28 Costimulation: From Mechanism to Therapy
- PMID: 27192564
- PMCID: PMC4932896
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.04.020
CD28 Costimulation: From Mechanism to Therapy
Abstract
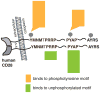
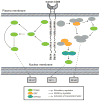
Ligation of the CD28 receptor on T cells provides a critical second signal alongside T cell receptor (TCR) ligation for naive T cell activation. Here, we discuss the expression, structure, and biochemistry of CD28 and its ligands. CD28 signals play a key role in many T cell processes, including cytoskeletal remodeling, production of cytokines, survival, and differentiation. CD28 ligation leads to unique epigenetic, transcriptional, and post-translational changes in T cells that cannot be recapitulated by TCR ligation alone. We discuss the function of CD28 and its ligands in both effector and regulatory T cells. CD28 is critical for regulatory T cell survival and the maintenance of immune homeostasis. We outline the roles that CD28 and its family members play in human disease and we review the clinical efficacy of drugs that block CD28 ligands. Despite the centrality of CD28 and its family members and ligands to immune function, many aspects of CD28 biology remain unclear. Translation of a basic understanding of CD28 function into immunomodulatory therapeutics has been uneven, with both successes and failures. Such real-world results might stem from multiple factors, including complex receptor-ligand interactions among CD28 family members, differences between the mouse and human CD28 families, and cell-type specific roles of CD28 family members.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Acuto O, Michel F. CD28-mediated co-stimulation: a quantitative support for TCR signalling. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3:939–951. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez-Quiroga C, Abud-Mendoza C, Doniz-Padilla L, Juarez-Reyes A, Monsivais-Urenda A, Baranda L, Gonzalez-Amaro R. CTLA-4-Ig therapy diminishes the frequency but enhances the function of Treg cells in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Immunol. 2011;31:588–595. - PubMed
-
- Andres PG, Howland KC, Nirula A, Kane LP, Barron L, Dresnek D, Sadra A, Imboden J, Weiss A, Abbas AK. Distinct regions in the CD28 cytoplasmic domain are required for T helper type 2 differentiation. Nat Immunol. 2004;5:435–442. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

