Intraindividual dynamics of transcriptome and genome-wide stability of DNA methylation
- PMID: 27192970
- PMCID: PMC4872231
- DOI: 10.1038/srep26424
Intraindividual dynamics of transcriptome and genome-wide stability of DNA methylation
Abstract
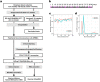
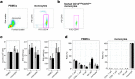
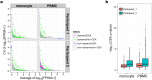
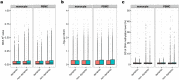
Cytosine methylation at CpG dinucleotides is an epigenetic mechanism that affects the gene expression profiles responsible for the functional differences in various cells and tissues. Although gene expression patterns are dynamically altered in response to various stimuli, the intraindividual dynamics of DNA methylation in human cells are yet to be fully understood. Here, we investigated the extent to which DNA methylation contributes to the dynamics of gene expression by collecting 24 blood samples from two individuals over a period of 3 months. Transcriptome and methylome association analyses revealed that only ~2% of dynamic changes in gene expression could be explained by the intraindividual variation of DNA methylation levels in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and purified monocytes. These results showed that DNA methylation levels remain stable for at least several months, suggesting that disease-associated DNA methylation markers are useful for estimating the risk of disease manifestation.
Figures
References
-
- Shiota K. DNA methylation profiles of CpG islands for cellular differentiation and development in mammals. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 105, 325–334 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Talens R. P. et al. Variation, patterns, and temporal stability of DNA methylation: considerations for epigenetic epidemiology. FASEB J. 24, 3135–3144 (2010). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

