CD8+ T Cell Breadth and Ex Vivo Virus Inhibition Capacity Distinguish between Viremic Controllers with and without Protective HLA Class I Alleles
- PMID: 27194762
- PMCID: PMC4944274
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00276-16
CD8+ T Cell Breadth and Ex Vivo Virus Inhibition Capacity Distinguish between Viremic Controllers with and without Protective HLA Class I Alleles
Abstract
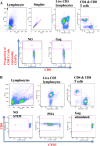
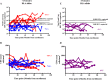
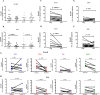
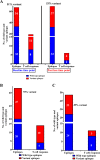
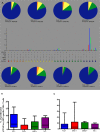
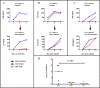
The mechanisms of viral control and loss of viral control in chronically infected individuals with or without protective HLA class I alleles are not fully understood. We therefore characterized longitudinally the immunological and virological features that may explain divergence in disease outcome in 70 HIV-1 C-clade-infected antiretroviral therapy (ART)-naive South African adults, 35 of whom possessed protective HLA class I alleles. We demonstrate that, over 5 years of longitudinal study, 35% of individuals with protective HLA class I alleles lost viral control compared to none of the individuals without protective HLA class I alleles (P = 0.06). Sustained HIV-1 control in patients with protective HLA class I alleles was characteristically related to the breadth of HIV-1 CD8(+) T cell responses against Gag and enhanced ability of CD8(+) T cells to suppress viral replication ex vivo In some cases, loss of virological control was associated with reduction in the total breadth of CD8(+) T cell responses in the absence of differences in HIV-1-specific CD8(+) T cell polyfunctionality or proliferation. In contrast, viremic controllers without protective HLA class I alleles possessed reduced breadth of HIV-1-specific CD8(+) T cell responses characterized by reduced ability to suppress viral replication ex vivo These data suggest that the control of HIV-1 in individuals with protective HLA class I alleles may be driven by broad CD8(+) T cell responses with potent viral inhibitory capacity while control among individuals without protective HLA class I alleles may be more durable and mediated by CD8(+) T cell-independent mechanisms.
Importance: Host mechanisms of natural HIV-1 control are not fully understood. In a longitudinal study of antiretroviral therapy (ART)-naive individuals, we show that those with protective HLA class I alleles subsequently experienced virologic failure compared to those without protective alleles. Among individuals with protective HLA class I alleles, viremic control was associated with broad CD8(+) T cells that targeted the Gag protein, and CD8(+) T cells from these individuals exhibited superior virus inhibition capacity. In individuals without protective HLA class I alleles, HIV-1-specific CD8(+) T cell responses were narrow and poorly inhibited virus replication. These results suggest that broad, highly functional cytotoxic T cells (cytotoxic T lymphocytes [CTLs]) against the HIV-1 Gag protein are associated with control among those with protective HLA class I alleles and that loss of these responses eventually leads to viremia. A subset of individuals appears to have alternative, non-CTL mechanisms of viral control. These controllers may hold the key to an effective HIV vaccine.
Copyright © 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures

References
-
- UNAIDS. 2013. Global report: UNAIDS report on the global AIDS epidemic 2013. UNAIDS, Geneva, Switzerland.
-
- Schmitz JE, Kuroda MJ, Santra S, Sasseville VG, Simon MA, Lifton MA, Racz P, Tenner-Racz K, Dalesandro M, Scallon BJ, Ghrayeb J, Forman MA, Montefiori DC, Rieber EP, Letvin NL, Reimann KA. 1999. Control of viremia in simian immunodeficiency virus infection by CD8+ lymphocytes. Science 283:857–860. doi:10.1126/science.283.5403.857. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kiepiela P, Leslie AJ, Honeyborne I, Ramduth D, Thobakgale C, Chetty S, Rathnavalu P, Moore C, Pfafferott KJ, Hilton L, Zimbwa P, Moore S, Allen T, Brander C, Addo MM, Altfeld M, James I, Mallal S, Bunce M, Barber LD, Szinger J, Day C, Klenerman P, Mullins J, Korber B, Coovadia HM, Walker BD, Goulder PJR. 2004. Dominant influence of HLA-B in mediating the potential co-evolution of HIV and HLA. Nature 432:769–775. doi:10.1038/nature03113. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kiepiela P, Ngumbela K, Thobakgale C, Ramduth D, Honeyborne I, Moodley E, Reddy S, de Pierres C, Mncube Z, Mkhwanazi N, Bishop K, van der Stok M, Nair K, Khan N, Crawford H, Payne R, Leslie A, Prado J, Prendergast A, Frater J, McCarthy N, Brander C, Learn GH, Nickle D, Rousseau C, Coovadia H, Mullins JI, Heckerman D, Walker BD, Goulder P. 2007. CD8+ T-cell responses to different HIV proteins have discordant associations with viral load. Nat Med 13:46–53. doi:10.1038/nm1520. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

