Regulatory T Cell Dysfunction Acquiesces to BTLA+ Regulatory B Cells Subsequent to Oral Intervention in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis
- PMID: 27194787
- PMCID: PMC4893905
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1501973
Regulatory T Cell Dysfunction Acquiesces to BTLA+ Regulatory B Cells Subsequent to Oral Intervention in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis
Abstract
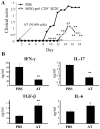
Regulatory T cells (Tregs) induced during autoimmunity often become quiescent and unable to resolve disease, suggesting inadequate activation. Resolution of established experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) can be achieved with myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG) fused to reovirus protein σ1 (MOG-pσ1), which activates Tregs, restoring protection, but requiring other regulatory cells to revitalize them. B cells have a dichotomous role in both the pathogenesis and recovery from EAE. Although inflammatory B cells contribute to EAE's pathogenesis, treatment of EAE mice with MOG-pσ1, but not OVA-pσ1, resulted in an influx of IL-10-producing B220(+)CD5(+) B regulatory cells (Bregs) enabling Tregs to recover their inhibitory activity, and in turn, leading to the rapid amelioration of EAE. These findings implicate direct interactions between Bregs and Tregs to facilitate this recovery. Adoptive transfer of B220(+)CD5(-) B cells from MOG-pσ1-treated EAE or Bregs from PBS-treated EAE mice did not resolve disease, whereas the adoptive transfer of MOG-pσ1-induced B220(+)CD5(+) Bregs greatly ameliorated EAE. MOG-pσ1-, but not OVA-pσ1-induced IL-10-producing Bregs, expressed elevated levels of B and T lymphocyte attenuator (BTLA) relative to CD5(-) B cells, as opposed to Tregs or effector T (Teff) cells, whose BTLA expression was not affected. These induced Bregs restored EAE Treg function in a BTLA-dependent manner. BTLA(-/-) mice showed more pronounced EAE with fewer Tregs, but upon adoptive transfer of MOG-pσ1-induced BTLA(+) Bregs, BTLA(-/-) mice were protected against EAE. Hence, this evidence shows the importance of BTLA in activating Tregs to facilitate recovery from EAE.
Copyright © 2016 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Figures
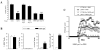






Similar articles
-
Active immunization using a single dose immunotherapeutic abates established EAE via IL-10 and regulatory T cells.Eur J Immunol. 2011 Feb;41(2):313-23. doi: 10.1002/eji.201041104. Epub 2010 Dec 29. Eur J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21268002 Free PMC article.
-
Tolerogen-induced interferon-producing killer dendritic cells (IKDCs) protect against EAE.J Autoimmun. 2011 Dec;37(4):328-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2011.09.005. Epub 2011 Oct 22. J Autoimmun. 2011. PMID: 22018711 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory B Cells Induce Formation of IL-10-Expressing T Cells in Mice with Autoimmune Neuroinflammation.J Neurosci. 2016 Dec 14;36(50):12598-12610. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1994-16.2016. Epub 2016 Nov 7. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27821578 Free PMC article.
-
The multiple faces of CD5.J Leukoc Biol. 2019 May;105(5):891-904. doi: 10.1002/JLB.MR0618-226R. Epub 2019 Jan 24. J Leukoc Biol. 2019. PMID: 30676652 Review.
-
The role of B regulatory (B10) cells in inflammatory disorders and their potential as therapeutic targets.Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Jan;78:106111. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.106111. Epub 2019 Dec 24. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31881524 Review.
Cited by
-
B Cell Regulation in Autoimmune Diseases.Acta Naturae. 2018 Jul-Sep;10(3):11-22. Acta Naturae. 2018. PMID: 30397522 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory B and T lymphocytes in multiple sclerosis: friends or foes?Auto Immun Highlights. 2018 Nov 10;9(1):9. doi: 10.1007/s13317-018-0109-x. Auto Immun Highlights. 2018. PMID: 30415321 Free PMC article. Review.
-
B- and T-Lymphocyte Attenuator Expression on Regulatory T-Cells in Patients with Severe Sepsis.Chin Med J (Engl). 2018 Nov 5;131(21):2637-2639. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.244104. Chin Med J (Engl). 2018. PMID: 30381607 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Role of TFH Cells in Promoting T Helper 17-Induced Neuroinflammation.Front Immunol. 2018 Feb 27;9:382. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00382. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29535739 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory B Cells in Pregnancy: Lessons from Autoimmunity, Graft Tolerance, and Cancer.Front Immunol. 2017 Feb 17;8:172. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00172. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28261223 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Edwards JC, G. Cambridge Sustained improvement in rheumatoid arthritis following a protocol designed to deplete B lymphocytes. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2001;40:205–211. - PubMed
-
- Looney RJ, Anolik JH, Campbell D, Felgar RE, Young F, Arend LJ, Sloand JA, Rosenblatt J, Sanz I. B cell depletion as a novel treatment for systemic lupus erythematosus: a phase I/II dose-escalation trial of rituximab. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50:2580–2589. - PubMed
-
- Hauser SL, Waubant E, Arnold DL, Vollmer T, Antel J, Fox RJ, Bar-Or A, Panzara M, Sarkar N, Agarwal S, Langer-Gould A, Smith CH, H. T. Group B-cell depletion with rituximab in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:676–688. - PubMed
-
- Evans JG, Chavez-Rueda KA, Eddaoudi A, Meyer-Bahlburg A, Rawlings DJ, Ehrenstein MR, Mauri C. Novel suppressive function of transitional 2 B cells in experimental arthritis. J Immunol. 2007;178:7868–7878. - PubMed
-
- Kala M, Rhodes SN, Piao WH, Shi FD, Campagnolo DI, Vollmer TL. B cells from glatiramer acetate-treated mice suppress experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Exp Neurol. 2010;221:136–145. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

