A continuous spectrophotometric assay that distinguishes between phospholipase A1 and A2 activities
- PMID: 27194811
- PMCID: PMC4959851
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.D065961
A continuous spectrophotometric assay that distinguishes between phospholipase A1 and A2 activities
Abstract
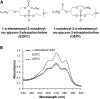
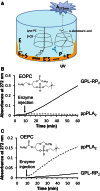
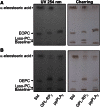
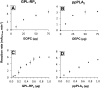
A new spectrophotometric assay was developed to measure, continuously and specifically, phospholipase A1 (PLA1) or phospholipase A2 (PLA2) activities using synthetic glycerophosphatidylcholines (PCs) containing α-eleostearic acid, either at the sn-1 position [1-α-eleostearoyl-2-octadecyl-rac-glycero-3-phosphocholine (EOPC)] or at the sn-2 position [1-octadecyl-2-α-eleostearoyl-rac-glycero-3-phosphocholine (OEPC)]. The substrates were coated onto the wells of microtiter plates. A nonhydrolyzable ether bond, with a non-UV-absorbing alkyl chain, was introduced at the other sn position to prevent acyl chain migration during lipolysis. Upon enzyme action, α-eleostearic acid is liberated and then solubilized into the micellar phase. The PLA1 or PLA2 activity was measured by the increase in absorbance at 272 nm due to the transition of α-eleostearic acid from the adsorbed to the soluble state. EOPC and OEPC differentiate, with excellent accuracy, between PLA1 and PLA2 activity. Lecitase(®), guinea pig pancreatic lipase-related protein 2 (known to be a PLA1 enzyme), bee venom PLA2, and porcine pancreatic PLA2 were all used to validate the assay. Compared with current assays used for continuously measuring PLA1 or PLA2 activities and/or their inhibitors, the development of this sensitive enzymatic method, using coated PC substrate analogs to natural lipids and based on the UV spectroscopic properties of α-eleostearic acid, is a significant improvement.
Keywords: 1-octadecyl-2-α-eleostearoyl-rac-glycero-3-phosphocholine; 1-α-eleostearoyl-2-octadecyl-rac-glycero-3-phosphocholine; tung oil; α-eleostearic acid; β-cyclodextrin.
Copyright © 2016 by the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
α-Eleostearic acid-containing triglycerides for a continuous assay to determine lipase sn-1 and sn-3 regio-preference.Chem Phys Lipids. 2017 Aug;206:43-52. doi: 10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2017.06.005. Epub 2017 Jun 16. Chem Phys Lipids. 2017. PMID: 28629973
-
A Continuous and Sensitive Spectrophotometric Assay for Lipase and Phospholipase A Activities Using α-Eleostearic Acid-Containing Substrates.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1835:119-128. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-8672-9_5. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 30109648
-
Development of a high-throughput assay for measuring phospholipase A activity using synthetic 1,2-α-eleostearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine coated on microtiter plates.Anal Chem. 2014 Nov 4;86(21):10576-83. doi: 10.1021/ac502096v. Epub 2014 Oct 13. Anal Chem. 2014. PMID: 25266374
-
Insect venom phospholipases A1 and A2: Roles in the envenoming process and allergy.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2019 Feb;105:10-24. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2018.12.011. Epub 2018 Dec 21. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30582958 Review.
-
Current Knowledge on Mammalian Phospholipase A1, Brief History, Structures, Biochemical and Pathophysiological Roles.Molecules. 2022 Apr 12;27(8):2487. doi: 10.3390/molecules27082487. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35458682 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Screening of phospholipase A activity and its production by new actinomycete strains cultivated by solid-state fermentation.PeerJ. 2017 Jul 6;5:e3524. doi: 10.7717/peerj.3524. eCollection 2017. PeerJ. 2017. PMID: 28695068 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical characterization of an alkaline and detergent-stable Lipase from Fusarium annulatum Bugnicourt strain CBS associated with olive tree dieback.PLoS One. 2023 May 19;18(5):e0286091. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0286091. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37205651 Free PMC article.
-
Phospholipase Family Enzymes in Lung Cancer: Looking for Novel Therapeutic Approaches.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jun 19;15(12):3245. doi: 10.3390/cancers15123245. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37370855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Role of Newly Found Auxiliary Site in Phospholipase A1 from Thai Banded Tiger Wasp (Vespa affinis) in Its Enzymatic Enhancement: In Silico Homology Modeling and Molecular Dynamics Insights.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Aug 8;12(8):510. doi: 10.3390/toxins12080510. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32784438 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Murayama K., Kano K., Matsumoto Y., and Sugimori D.. 2013. Crystal structure of phospholipase A1 from Streptomyces albidoflavus NA297. J. Struct. Biol. 182: 192–196. - PubMed
-
- Hla T., Lee M. J., Ancellin N., Paik J. H., and Kluk M. J.. 2001. Lysophospholipids–receptor revelations. Science. 294: 1875–1878. - PubMed
-
- Yasuda T., Ishida T., and Rader D. J.. 2010. Update on the role of endothelial lipase in high-density lipoprotein metabolism, reverse cholesterol transport, and atherosclerosis. Circ. J. 74: 2263–2270. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

