Short Stature in Isodicentric Y Chromosome and Three Copies of the SHOX Gene: Clinical Report and Review of Literature
- PMID: 27194969
- PMCID: PMC4862393
- DOI: 10.1159/000444430
Short Stature in Isodicentric Y Chromosome and Three Copies of the SHOX Gene: Clinical Report and Review of Literature
Abstract
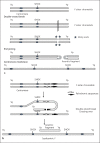
Short stature homeobox gene (SHOX) mutations and pseudoautosomal region 1 (PAR1) deletions encompassing SHOX are known causes of Léri-Weill dyschondrosteosis and isolated short stature, while 3 copies of SHOX in cases with triple sex chromosome constitution are responsible for tall stature. Duplications involving SHOX have been rarely reported, and they were found in individuals with short, normal and tall stature. An adopted boy with short stature, isodicentric Y chromosome and 3 copies of SHOX is described. Normal growth hormone (GH) secretion and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1) increase during an IGF1 generation test were found, ruling out impaired GH-IGF1 axis. No other organic or psychiatric causes of impaired growth were found. GH treatment improved linear growth, as reported in children with SHOX haploinsufficiency. This new report and the review of literature support that SHOX duplication may cause short stature, especially in those children with duplications of the 5'SHOX regulatory elements. Chromosome analysis and detailed molecular characterization of the duplicated region should be warranted in individuals with SHOX duplications in order to investigate the presence of occult chromosome imbalance. Additional reports and follow-up till adult height are needed to give conclusions on long-term efficacy and safety of GH treatment in short children with SHOX duplication.
Keywords: GH-IGF1 axis; SHOX; SHOX duplications; Short stature; Y chromosome rearrangement.
Figures

References
-
- Aksglaede L, Skakkebaek NE, Juul A. Abnormal sex chromosome constitution and longitudinal growth: serum levels of insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I, IGF binding protein-3, luteinizing hormone, and testosterone in 109 males with 47,XXY, 47,XYY, or sex-determining region of the Y chromosome (SRY)-positive 46,XX karyotypes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93:169–176. - PubMed
-
- Benito-Sanz S, Barroso E, Heine-Suñer D, Hisado-Oliva A, Romanelli V, et al. Clinical and molecular evaluation of SHOX/PAR1 duplications in Léri-Weill dyschondrosteosis (LWD) and idiopathic short stature (ISS). J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011;96:E404–E412. - PubMed
-
- Bertelloni S, Baroncelli GI, Dati E, Ghione S, Baldinotti F, et al. IGF-I generation test in prepubertal children with Noonan syndrome due to mutations in the PTPN11 gene. Hormones (Athens) 2013;12:86–92. - PubMed
-
- Binder G. Short stature due to SHOX deficiency: genotype, phenotype, and therapy. Horm Res Paediatr. 2011;75:81–89. - PubMed
-
- Blaschke RJ, Töpfer C, Marchini A, Steinbeisser H, Janssen JW, Rappold GA. Transcriptional and translational regulation of the Léri-Weill and Turner syndrome homeobox gene SHOX. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:47820–47826. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

