Apoptotic CD8 T-lymphocytes disable macrophage-mediated immunity to Trypanosoma cruzi infection
- PMID: 27195678
- PMCID: PMC4917666
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2016.135
Apoptotic CD8 T-lymphocytes disable macrophage-mediated immunity to Trypanosoma cruzi infection
Abstract
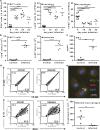
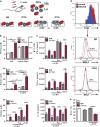
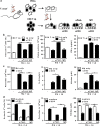
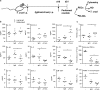
Chagas disease is caused by infection with the protozoan Trypanosoma cruzi. CD8 T-lymphocytes help to control infection, but apoptosis of CD8 T cells disrupts immunity and efferocytosis can enhance parasite infection within macrophages. Here, we investigate how apoptosis of activated CD8 T cells affects M1 and M2 macrophage phenotypes. First, we found that CD8 T-lymphocytes and inflammatory monocytes/macrophages infiltrate peritoneum during acute T. cruzi infection. We show that treatment with anti-Fas ligand (FasL) prevents lymphocyte apoptosis, upregulates type-1 responses to parasite antigens, and reduces infection in macrophages cocultured with activated CD8 T cells. Anti-FasL skews mixed M1/M2 macrophage profiles into polarized M1 phenotype, both in vitro and following injection in infected mice. Moreover, inhibition of T-cell apoptosis induces a broad reprogramming of cytokine responses and improves macrophage-mediated immunity to T. cruzi. The results indicate that disposal of apoptotic CD8 T cells increases M2-macrophage differentiation and contributes to parasite persistence.
Figures



References
-
- Coura JR, Vinas PA. Chagas disease: a new worldwide challenge. Nature 2010; 465: S6–S7. - PubMed
-
- Lescure FX, Le Loup G, Freilij H, Develoux M, Paris L, Brutus L et al. Chagas disease: changes in knowledge and management. Lancet Infect Dis 2010; 10: 556–570. - PubMed
-
- Morillo CA, Marin-Neto JA, Avezum A, Sosa-Estani S, Rassi A Jr., Rosas F et al. Randomized Trial of benznidazole for chronic chagas' cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med 2015; 373: 1295–1306. - PubMed
-
- Junqueira C, Caetano B, Bartholomeu DC, Melo MB, Ropert C, Rodrigues MM et al. The endless race between Trypanosoma cruzi and host immunity: lessons for and beyond Chagas disease. Expert Rev Mol Med 2010; 12: e29. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

