Postprandial C-Peptide to Glucose Ratio as a Marker of β Cell Function: Implication for the Management of Type 2 Diabetes
- PMID: 27196896
- PMCID: PMC4881566
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms17050744
Postprandial C-Peptide to Glucose Ratio as a Marker of β Cell Function: Implication for the Management of Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
C-peptide is secreted from pancreatic β cells at an equimolar ratio to insulin. Since, in contrast to insulin, C-peptide is not extracted by the liver and other organs, C-peptide reflects endogenous insulin secretion more accurately than insulin. C-peptide is therefore used as a marker of β cell function. C-peptide has been mainly used to assess the presence of an insulin-dependent state for the diagnosis of type 1 diabetes. However, recent studies have revealed that β cell dysfunction is also a core deficit of type 2 diabetes, and residual β cell function is a key factor in achieving optimal glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. This review summarizes the role of C-peptide, especially the postprandial C-peptide to glucose ratio which likely better reflects maximum β cell secretory capacity compared with the fasting ratio in assessing β cell function, and discusses perspectives on its clinical utility for managing glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Keywords: C-peptide; postprandial; type 2 diabetes; β cell function.
Figures

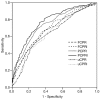
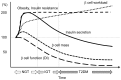
References
-
- International Diabetes Federation IDF Diabetes Atlas, 7th ed. [(accessed on 21 March 2016)]. Available online: http://www.idf.org/diabetesatlas.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

